Marine robotic platforms support various applications, including marine exploration, underwater infrastructure inspection, and ocean environment monitoring. While reliable perception systems enable robots to sense their surroundings, detect objects, and navigate complex underwater terrains independently, developing these systems presents unique difficulties compared to their terrestrial counterparts. Collecting real-world underwater data requires complex hardware, controlled experimental setups, and extensive fieldwork, making the process resource-intensive. Moreover, real-world testing can be impractical, hazardous, and expensive. Underwater simulation platforms have emerged as a promising alternative, providing researchers and engineers with controlled, repeatable, and scalable environments.
Existing attempts to address underwater perception challenges have focused on developing high-performance simulators, as real-world testing remains difficult and resource-intensive. Early underwater simulators built on ROS Gazebo offered hydrodynamic simulation but lacked high-fidelity visual rendering. More recent game engine-powered simulators like HoloOcean and UNav-Sim used Unreal Engine to improve rendering quality. NVIDIA Isaac Sim emerged as a high-performance alternative with GPU-accelerated robotics simulation, physics-based photorealistic rendering, and seamless integration with NVIDIA Omniverse and OpenUSD ecosystems. MarineGym extended Isaac Sim to underwater applications but focused on robot control tasks without providing open-source implementation.
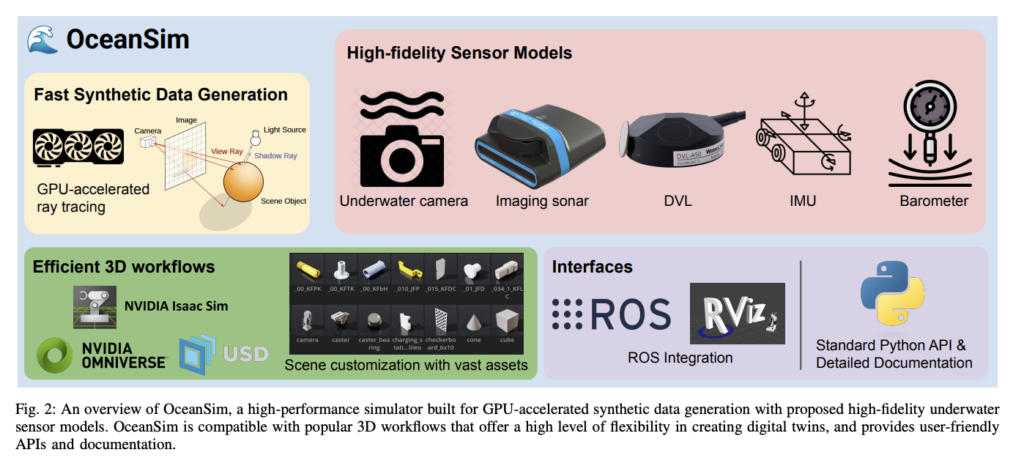
Researchers from the University of Michigan have proposed OceanSim, a high-performance underwater simulator accelerated by NVIDIA parallel computing technology. Built upon NVIDIA Isaac Sim, OceanSim leverages high-fidelity, physics-based rendering, and GPU-accelerated real-time ray tracing to create realistic underwater environments. It bridges underwater simulation with the rapidly expanding NVIDIA Omniverse ecosystem, enabling the application of multiple existing sim-ready assets and robot learning approaches within underwater robotics research. Moreover, OceanSim allows the user to operate the robot, visualize sensor data, and record data simultaneously during GPU-accelerated simulated data generation.
OceanSim utilizes NVIDIA’s powerful ecosystem, providing real-time GPU-accelerated ray tracing while allowing users to customize underwater environments and robotic sensor configurations. OceanSim implements specialized underwater sensor models to complement Isaac Sim’s built-in capabilities. These include an image formation model capturing water column effects across various water types, a GPU-based sonar model with realistic noise simulation for faster rendering, and a Doppler Velocity Log (DVL) model that simulates range-dependent adaptive frequency and dropout behaviors. For imaging sonar, OceanSim utilizes Omniverse Replicator for rapid synthetic data generation, establishing a virtual rendering viewport that retrieves scene geometry information through GPU-accelerated ray tracing
Using HoloOcean’s official v1.0 release and a reproduction of UNav-Sim’s rendering effects (UNav-Sim*), researchers evaluated underwater imaging quality by manually tuning parameters to match real underwater images. Results show that OceanSim consistently achieves the best or second-best RGB angular error across all test cases, validating the accuracy of its underwater image rendering pipeline. For sonar performance, OceanSim outperforms HoloOcean in rendering speed. While HoloOcean requires building a partial octree cache on first startup of new scenes, adding considerable overhead time, OceanSim leverages GPU-based ray tracing to achieve real-time sonar rendering without requiring extra cache-building time.
In conclusion, researchers introduced OceanSim, a high-performance underwater simulation framework. Its highly flexible 3D workflows provide significant advantages, and researchers plan to release OceanSim with comprehensive documentation to support the marine robotics research community. Despite these achievements, OceanSim has limitations. As a perception-oriented simulator, it currently lacks accurate modeling of underwater vehicle dynamics and fluid dynamics. The beta release primarily targets developers, requiring coding for new simulation scenarios rather than offering a user-friendly graphical interface. OceanSim lacks implementation of optical and acoustic communication modems for simulation of multi-agent cooperative scenarios.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 85k+ ML SubReddit.
The post University of Michigan Researchers Introduce OceanSim: A High-Performance GPU-Accelerated Underwater Simulator for Advanced Marine Robotics appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on OPEN SOURCE AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 3 Hour Short Event (April 12, 9 am- 12 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop [Sponsored]
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on OPEN SOURCE AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 3 Hour Short Event (April 12, 9 am- 12 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop [Sponsored]