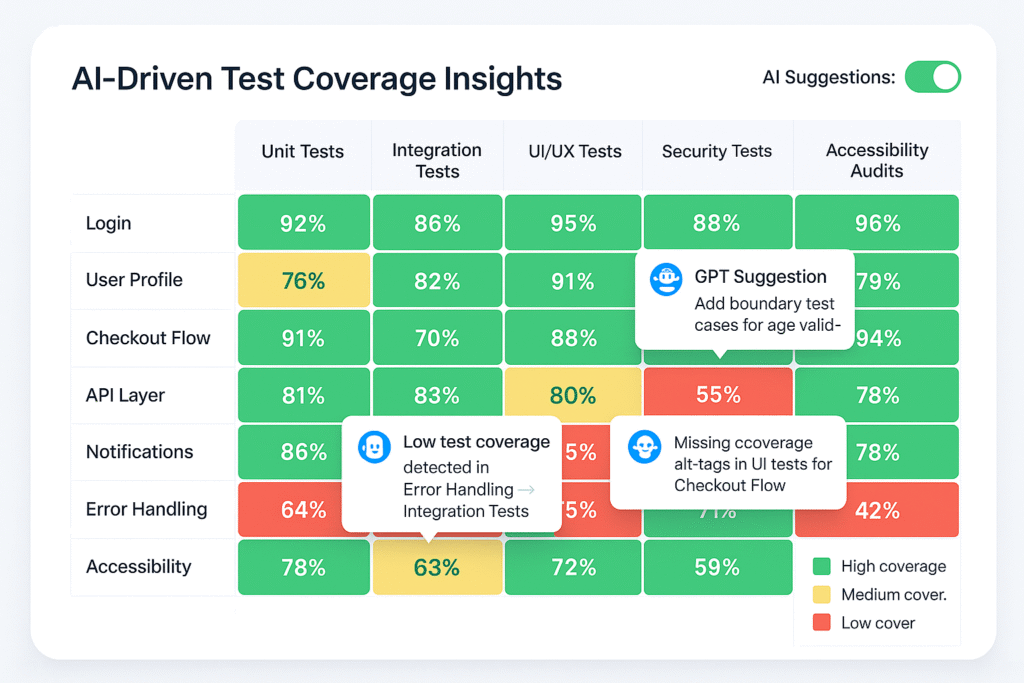
The Microsoft 365 Admin Center is the centralized web-based portal administrators use to manage Microsoft 365 services for their organization. It provides a single access point for managing users, licenses, apps, and services like Exchange Online, Outlook, SharePoint, Teams, and more.
Key Functions of the Admin Center
- User Management: Add, remove, or edit user accounts and assign licenses.
- License Management: Purchase, assign, and monitor licenses across the organization.
- Service Health Monitoring: View the status of Microsoft services and receive incident reports.
- Billing and Subscriptions: Manage subscriptions, payment methods, and invoices.
- Security & Compliance: Access tools to enforce data protection, compliance policies, and user security.
- Reports & Insights: Generate usage, adoption, and security trends reports.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): For better governance, assign different admin roles, such as Global Admin, User Admin, Billing Admin, etc.
- Settings Configuration: Configure settings for Microsoft Teams, Exchange, and SharePoint services.
10 Best Practices for User and Group Management in Microsoft 365
Effectively managing users and groups is key to maintaining security, compliance, and operational efficiency within Microsoft 365. Below are 10 best practices to follow:
1. Follow the Principle of Least Privilege
- Assign only the permissions a user needs to perform their job.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) instead of giving everyone Global Admin rights.
- Delegated roles like User Admin, Groups Admin, Helpdesk Admin, etc., as needed.
2. Standardize User Creation
- Use a user creation template or naming convention (e.g., firstname.lastname@company.com).
- Automate user provisioning through tools like Azure AD Connect or Microsoft Entra ID.
- Set password policies and MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication), and assign licenses upon creation.
3. Organize Users with Security and Microsoft 365 Groups
- Use:
- Microsoft 365 Groups for collaboration in Teams, Outlook, and SharePoint.
- Security Group for resource access control (e.g., OneDrive, SharePoint).
- -Mail-Enabled Security Groups are available when email is needed with access control.
- Avoid group sprawl by regularly reviewing unused or duplicate groups.
4. Use Dynamic Groups Where Possible
- Dynamic groups automatically add or remove users based on attributes such as department or job title.
- Helps keep access rights consistent and minimizes manual errors.
5. Review and Audit Access Regularly
- Perform periodic access reviews using Azure AD Access Reviews.
- Audit group memberships, admin roles, and license assignments.
6. Implement Group Naming Policies
- Create consistent and clear group names, e.g., ‘HR-Team-M365’, ‘IT-Admins.’
- Use Entra ID (Azure AD) naming policies to enforce this automatically.
7. Monitor and Log User Activity
- Use Microsoft 365 audit logs and Microsoft Purview to track user and admin actions.
- Enable logging for sign-ins, password resets, file access, etc.
8. Secure Admin Accounts
- Use Privileged Identity Management (PIM) to elevate roles only when needed.
- Require MFA for all admin accounts.
- Consider dedicated admin accounts separate from users’ day-to-day login accounts.
9. Use Expiration Policies for Guest Users and Groups
- Set expiration policies to automatically clean up old groups or guest accounts.
- Helps reduce risk and clutter in your directory.
10. Document Changes and Procedures
- Maintain internal documentation for user/group management procedures.
- Helps onboard new IT staff and ensures consistency across the team.
Managing Licenses and Subscriptions in the Microsoft 365 Admin Center
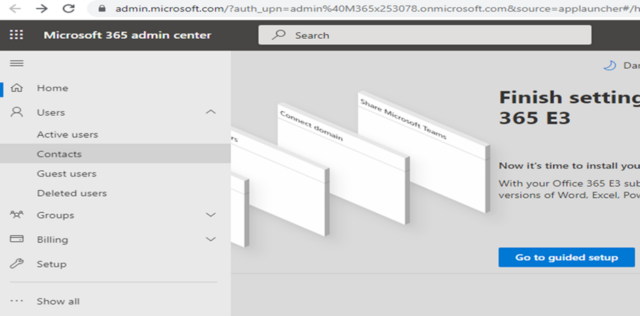
1. Accessing License and Subscription Information
- Sign in at [admin.microsoft.com] with admin credentials.
- Navigate to:
- Billing > Your Products – to view active subscriptions.
- Billing > Licenses – to view how many licenses are available, assigned, or unused.
- Users > Active Users – to manage user license assignments directly.
2. Assigning Licenses to Users
- Go to Users > Active Users.
- Select a user and click Licenses and Apps.
- You can choose the subscription (e.g., Microsoft 365 E3) and turn on/off specific apps like Teams, SharePoint, etc.
- Click Save changes.
3. Assigning Licenses to Groups (Recommended for Automation)
- Use Group-based licensing (requires Azure AD P1 or P2).
- Go to Groups > Active Groups.
- Select a security or Microsoft 365 group, then choose Licenses.
- Assign the desired license(s) and click Save.
Note: When users join the group, licenses are auto-assigned. When they leave, licenses are removed.
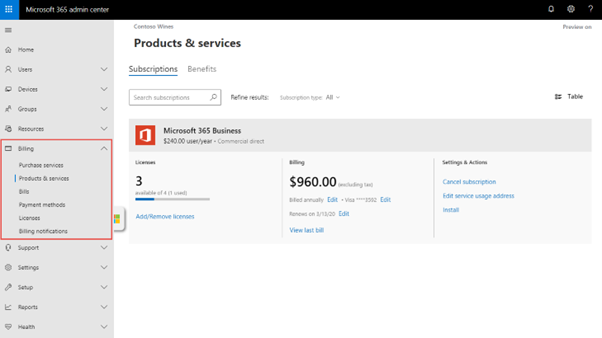
4. Managing Subscriptions
- Go to Billing > Your Products to:
- View subscription names (e.g., Microsoft 365 Business Premium).
- Check the number of licenses purchased and in use.
- Renew or cancel subscriptions.
- Add or reduce license count.
- Assign add-ons like Audio Conferencing, Defender for Office 365, etc.
5. Monitoring License Usage
- Navigate to Billing > Licenses to:
- View total vs. assigned vs. available licenses.
- Download usage reports.
- Go to Reports > Usage for more insights into how services (like Teams or OneDrive) are used.
6. Removing/Reassigning Licenses
- When a user leaves:
- Go to Users > Active Users> select the user.
- Remove the license and optionally delete the account.
Best practice tip: Transfer any data (email, OneDrive) before deletion or license removal.
7. Setting License Expiration Alerts
- Enable billing notifications under Billing > Billing Notifications.
- Set up alerts in Microsoft Purview or Defender for unused or about-to-expire licenses.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in Microsoft 365
What is RBAC?
Role-based access Control in Microsoft 365 allows you to assign specific permissions to users based on their job roles without giving them full administrative access. This is a best practice for security, compliance, and operational efficiency.
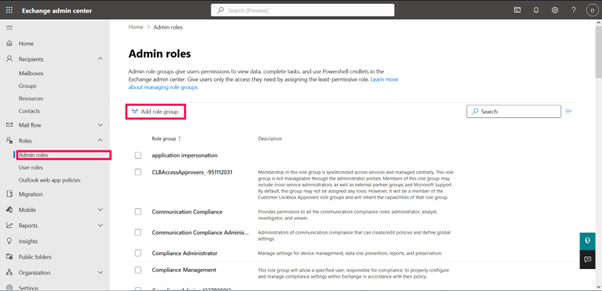
Where is RBAC Configured?
RBAC is configured in:
- Microsoft 365 Admin Center
- Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD)
- Exchange Admin Center (EAC)
- Security & Compliance Center
Key Admin Roles in Microsoft 365
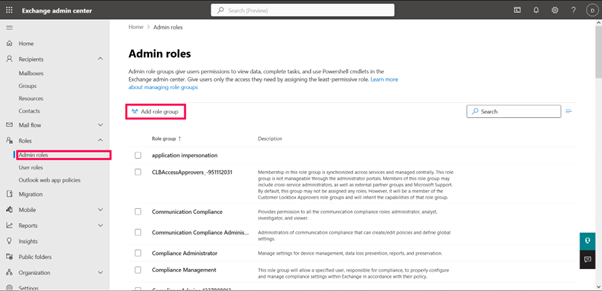
- Global Administrator: Has full access to all M365 services and settings. Use sparingly.
- User Administrator: Manage user accounts, groups, and licenses.
- Group Administrator: Manage Microsoft 365 groups and distribution lists.
- Helpdesk Administrator: Reset passwords and manage support tickets.
- Billing Administrator: Manage subscriptions, billing, and payments.
- Compliance Administrator: Access Microsoft Purview and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) settings.
- Security Administrator: Manage security settings and Microsoft Defender.
- Exchange Administrator: Configures mailboxes, transport rules, and Exchange settings.
- SharePoint Administrator: Manage SharePoint sites and settings.
- Teams Administrator: Configure Microsoft Teams policies, voice, and settings.
How to Assign Roles in the Microsoft 365 Admin Center
- Go to [admin.microsoft.com
- Navigate to Users > Active Users
- Click on the user → go to Roles
- Choose either:
- Global Admin
- Privileged Role
- Or search for a specific role
- Click Save changes
Advanced RBAC with Microsoft Entra (Azure AD)
For finer control, use:
- PIM (Privileged Identity Management): Grant “just-in-time” access to roles
- Custom roles: Create your own roles with specific permissions
- Administrative units (AUs): Delegate control based on geography, department, etc.
Best Practices for RBAC in Microsoft 365
- Use the least privilege model: Minimize attack surface.
- Assign roles to groups: Easier to manage at scale.
- Monitor role assignments regularly: Catch role creep and misconfigurations.
- Use PIM for elevated roles: Limit exposure of critical permissions.
- Document who has what role: For transparency and audits.
Understanding Security & Compliance in Microsoft 365
Microsoft 365 provides robust tools under the Microsoft Purview (formerly Security & Compliance Center) and Microsoft Defender platforms to help organizations secure data, detect threats, and ensure compliance.
1. Core Security Features
Microsoft Defender for Office 365
- Protects against phishing, malware, and ransomware
- Features: Safe Attachments, Safe Links, Threat Investigation & Response
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Requires users to verify identity via a second factor (e.g., phone, app)
Conditional Access
- Control resource access based on user location, device compliance, risk level, etc.
Identity Protection
- Detects risky sign-ins and users using machine learning
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Advanced threat protection for devices
- Includes endpoint detection and response (EDR)
Secure Score
- Microsoft’s security health check for your environment
- Recommend actions to improve your security posture
2. Compliance Features via Microsoft Purview
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- Monitors and restricts sharing of sensitive data (e.g., credit card numbers, SSNs)
- Works across Exchange, SharePoint, OneDrive, Teams
Information Protection & Sensitivity Labels
- Classify and protect content based on its sensitivity
- Applies encryption, watermarks, or access controls automatically
Retention Policies
- Keeps or deletes data based on business or legal requirements
- Applies to email, Teams, OneDrive, SharePoint
eDiscovery
- Allows legal teams to search and preserve data for investigations or litigation
Audit Logging
- Tracks user and admin activity (e.g., file access, sign-in attempts)
- Essential for forensic analysis and incident response
Insider Risk Management
- Detects potential insider threats like data leaks or policy violations
Compliance Score
- Tracks your compliance with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001
Source: Read MoreÂ