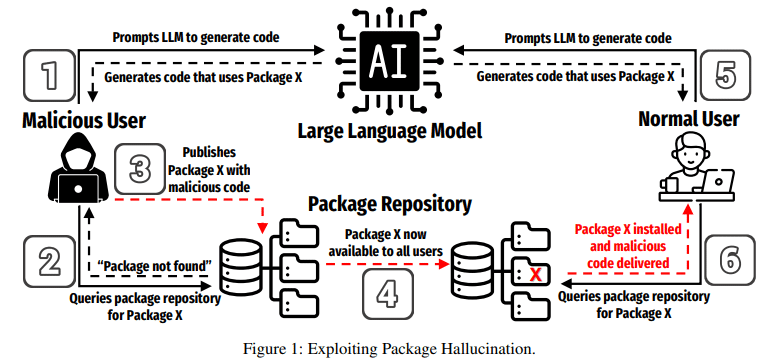
Code-generating large language models (LLMs) have introduced a new security issue into software development: Code package hallucinations.
Package hallucinations occur when an LLM generates code that references a package that doesn’t actually exist, creating an opportunity for threat actors to exploit that GenAI hallucination by creating a malicious repository with the same name as the hallucinated package.
Researchers at the University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA), the University of Oklahoma and Virginia Tech, detailed the package hallucination phenomenon in a paper published on arXiv last month – including some strategies for detecting hallucinated packages in code.
Code Package Hallucinations Can Occur More than 20% of the Time
While most research has focused on hallucinations in natural language generation and prediction tasks, the occurrence of hallucinations during code generation and the implications for code security “are still in the nascent stages of research,” the researchers said.
Chinese researchers last year showed that LLMs such as ChatGPT, CodeRL, and CodeGen can significantly hallucinate during code generation.
The new research, headed by UTSA’s Joseph Spracklen, looks specifically at the problem of package hallucination.
“These hallucinations, which arise from fact-conflicting errors when generating code using LLMs, represent a novel form of package confusion attack that poses a critical threat to the integrity of the software supply chain,” they wrote.
The researchers looked at 16 popular LLMs for code generation – among them ChatGPT, CodeLlama and DeepSeek – and found that “the average percentage of hallucinated packages is at least 5.2% for commercial models and 21.7% for open-source models.”
Their tests in Python and JavaScript generated a total of 2.23 million packages in response to prompts, of which 440,445 (19.7%) were determined to be hallucinations, including “a staggering 205,474 unique examples of hallucinated package names, further underscoring the severity and pervasiveness of this threat.”
“An adversary can exploit package hallucinations, especially if they are repeated, by publishing a package to an open-source repository with the same name as the hallucinated or fictitious package and containing some malicious code/functionality,” they said. “As other unsuspecting and trusting LLM users are subsequently recommended the same fictitious package in their generated code, they end up downloading the adversary-created malicious package, resulting in a successful compromise. This compromise can then spread through an entire codebase or software dependency chain, infecting any code that relies on the malicious package.”
Detecting Code Package Hallucinations
The researchers noted that simply comparing a package name with a list of known packages is ineffective because an adversary may have already published under the hallucinated package name. Their research used three heuristics that provided specific package names, after which “we simply compare each package name to a master list of package names acquired from PyPI and npm, respectively… If a package name is not on the master list, it is considered a hallucination.”
“We acknowledge the possibility that the master list of packages obtained from the package repositories has already been contaminated with malicious hallucinated packages,” the researchers wrote. “It is not possible to guarantee that the master list actually represents the ground truth of valid packages; however, the presence of hallucinated packages already in the master list would actually produce fewer hallucinations, and therefore our results represent a lower bound of hallucination rate.”
The researchers were able to reduce code package hallucinations by as much as 85% using mitigation strategies.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and supervised fine-tuning turned out to be the most effective approaches for reducing package hallucination, but the mitigation techniques came at the cost of code quality.
“In summary, our results demonstrate that while all tested mitigation strategies effectively reduce package hallucinations, fine-tuning comes at the cost of diminished code quality,” they said. “Further research is needed to develop fine-tuning methods that minimize hallucinations without compromising quality. In the meantime, RAG and self-refinement offer promising alternatives.”
With surveys showing as many as 97% of developers using GenAI tools to some degree in code development, the need for effective error mitigation strategies will only increase.
Source: Read More