Natural language interface to databases is a growing focus within artificial intelligence, particularly because it allows users to interact with structured databases using plain human language. This area, often known as NL2SQL (Natural Language to SQL), is centered on transforming user-friendly queries into SQL commands that can be directly executed on databases. The objective is to simplify data access for non-technical users and broaden the utility of data systems in various sectors like finance, healthcare, and retail. With the rise of LLMs, significant progress has made these conversions more accurate and context-aware, especially when dealing with simple queries or structured database layouts.
Despite progress, converting natural language into accurate SQL remains difficult in complex situations involving multiple table joins, nested queries, or ambiguous semantics. The challenge is not just about generating syntactically correct SQL but producing queries that correctly reflect the user’s intent and can be generalized across domains. Standard approaches struggle to scale in high-stakes fields where interpretability and precision are critical. Moreover, many current models depend heavily on fixed schemas and training data structures, which hampers their performance in new or evolving environments.
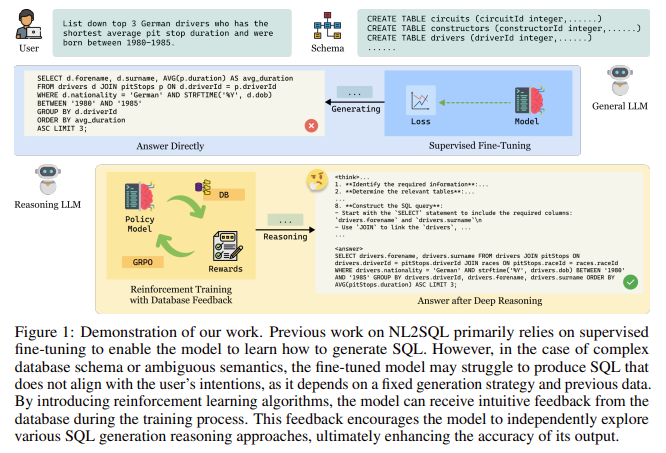
Most NL2SQL systems today rely on supervised fine-tuning, where large language models are trained on annotated datasets that pair questions with correct SQL answers. While this method has led to noticeable improvements, it introduces limitations in adaptability and interpretability. Because these models are tuned to specific datasets and schemas, they often fail in unfamiliar scenarios. Also, they follow a rigid generation strategy, which can lead to failures when the input diverges from training data. These systems also typically lack transparency in their reasoning processes, limiting their utility in domains where clear decision-making trails are necessary.
Researchers from IDEA Research, the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou), the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and DataArc Tech Ltd. introduced SQL-R1. This new NL2SQL model leverages reinforcement learning rather than traditional supervised learning. SQL-R1 uses feedback mechanisms during training to improve its performance. Instead of just learning from annotated examples, the model learns by generating SQL candidates, executing them, and receiving structured feedback on the outcome. This feedback includes whether the SQL was syntactically correct, whether it produced the proper result, and how efficient and interpretable it was. This dynamic learning process allows the model to optimize its SQL generation strategies over time and improves generalization in complex or unfamiliar scenarios.
To build SQL-R1, researchers first performed supervised fine-tuning on 200,000 samples drawn from a large synthetic dataset called SynSQL-2.5M. This process, known as a cold start, ensured the model could follow basic instructions and generate simple SQL outputs. Following this, reinforcement learning was introduced using the Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm. The model generated multiple SQL candidates for each query and was rewarded based on a composite scoring function. This function included four metrics: format reward (+1 or -1 depending on syntax correctness), execution reward (+2 for executable queries, -2 for failures), result reward (+3 for correct query outputs, -3 for incorrect ones), and length reward based on the depth and clarity of the reasoning trace. Each of these scores contributed to updating the model’s internal decision-making process.
SQL-R1 was evaluated on two industry-standard NL2SQL benchmarks: Spider and BIRD. On the Spider development set, the model achieved 87.6% execution accuracy, and on the Spider test set, it gained 88.7%. For the BIRD dataset, which covers 95 databases from 37 domains, the model scored 66.6%. These results are competitive with or superior to larger models, including closed-source solutions like GPT-4. Notably, SQL-R1 used the Qwen2.5-Coder-7B model, which is considerably smaller than many alternatives, demonstrating that high accuracy can be achieved with efficient architectures when combined with reinforcement learning. An ablation study confirmed the contribution of each reward component. Removing the format reward, for instance, caused accuracy to drop from 63.1% to 60.4%. Removing the result reward caused a 0.7% drop, indicating that each element in the reward mechanism plays a role in guiding the model.
Several Key Takeaways from the Research on SQL-R1:
- SQL-R1 achieved 88.7% accuracy on the Spider test set and 66.6% on the BIRD development set, using only a 7B base model (Qwen2.5-Coder-7B).
- The model used 200,000 samples from the SynSQL-2.5M dataset for supervised fine-tuning and 5,000 complex samples for reinforcement learning.
- The GRPO algorithm powered reinforcement learning, which required no value model and worked efficiently with relative performance scores.
- The reward function included four components: Format (+1/-1), Execution (+2/-2), Result (+3/-3), and Length (proportional).
- SQL-R1 outperformed larger models like GPT-4, highlighting that model architecture and feedback training are as critical as size.
- Ablation studies revealed the importance of each reward: removing the format reward caused a 2.7% drop in performance, while eliminating the execution reward dropped accuracy by 2.4%.
- The approach promotes transparency, as the model provides reasoning traces using ‘<think>’ and ‘<answer>’ tags, improving end-user interpretability.
Here is the Paper. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
The post SQL-R1: A Reinforcement Learning-based NL2SQL Model that Outperforms Larger Systems in Complex Queries with Transparent and Accurate SQL Generation appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop