Language models predict sequences of words based on vast datasets and are increasingly expected to reason and perform complex linguistic manipulations. Yet, despite their growing sophistication, even powerful models often falter when assigned problems that require step-by-step logic, especially those bound by explicit constraints or structured problem-solving, highlighting their current limitations in applied reasoning.
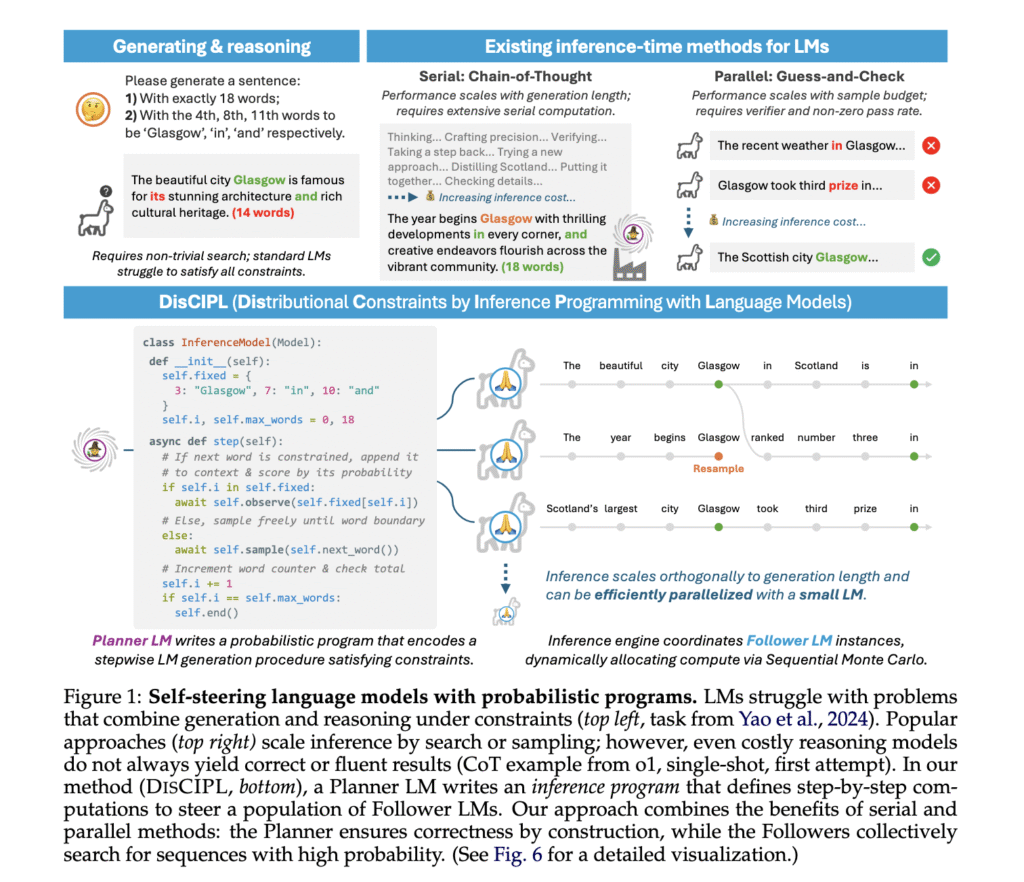
The difficulty arises in generating language that strictly adheres to given conditions. Tasks might specify exact word counts, position of keywords, or thematic constraints, all of which are challenging for models prioritizing probability-based fluency. For example, models often fail to construct a coherent sentence while embedding words at particular locations or composing paragraphs under multiple concurrent requirements. The challenge isn’t just generating relevant content but generating content that rigidly fits a set of formal, predefined rules without compromising fluency.
Currently, methods like chain-of-thought prompting attempt to guide models through a reasoning path, but these are limited by their serial execution and expensive inference costs. Parallel approaches such as guess-and-check or best-of-N sampling rely on generating and filtering multiple candidates. Yet, they need separate scoring mechanisms and often yield inconsistent results. These tools improve performance slightly but cannot guarantee the satisfaction of all constraints, especially when models lack an inherent understanding of those constraints.
Researchers from MIT and Yale introduced a novel approach named DISCIPL, designed to enable what they term “self-steering” language models. This method defines two roles: a Planner language model, which generates a tailored inference program, and a population of Follower models that execute this program to solve the task. Unlike previous systems, the Planner creates a logic that structures the reasoning process. By separating the planning from execution, the method allows for dynamic and adaptive computation strategies tailored to each task.
The inner workings of DISCIPL involve generating inference code using a language called LLAMPPL, which is a Python-based framework for probabilistic programming with language models. The Planner writes code that defines how to explore possible solutions, while Follower models run the code to search for valid outputs. These programs operate by iteratively proposing partial solutions and scoring them based on constraints. The architecture supports multiple inference techniques, including importance sampling, sequential Monte Carlo (SMC), and rejection sampling, which are scalable based on computational budgets. This structured decomposition lets the system reallocate resources to more promising candidates during execution, improving precision and efficiency.
In performance evaluations, DISCIPL proved remarkably effective. On the COLLIE benchmark for constrained sentence generation, the Follower model Llama-3.2-1B alone achieved only 4% Pass@1 success. When enhanced with DISCIPL and SMC, performance rose to 87%, surpassing GPT-4o-mini in some instances. The same setup scored as high as 88% Pass@1 for paragraph-level tasks. On a set of difficult real-world tasks called PUZZLES, covering grant writing and itinerary planning, DISCIPL consistently outperformed both the Planner and Follower operating alone. The method also demonstrated high coherency, with average scores around 7.45 out of 10 when using SMC, which starkly contrasts the 9+ scores from more fluent but incorrect outputs produced by baseline methods.
Overall, the work introduces a fresh direction in language modeling where models generate answers and devise how they should be computed. By letting the Planner generate code that structures reasoning and Followers execute this code in parallel, the method achieves precision, adaptability, and fluency without requiring larger models or manual engineering. The research’s results illustrate a clear path for enabling smaller language models to outperform their size through intelligent orchestration and self-guided inference.
Here is the Paper. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
The post MIT Researchers Introduce DISCIPL: A Self-Steering Framework Using Planner and Follower Language Models for Efficient Constrained Generation and Reasoning appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop