Designing intelligent systems that function reliably in dynamic physical environments remains one of the more difficult frontiers in AI. While significant advances have been made in perception and planning within simulated or controlled contexts, the real world is noisy, unpredictable, and resistant to abstraction. Traditional AI systems often rely on high-level representations detached from their physical implementations, leading to inefficiencies in response time, brittleness to unexpected changes, and excessive power consumption. In contrast, humans and animals exhibit remarkable adaptability through tight sensorimotor feedback loops. Reproducing even a fraction of that adaptability in embodied systems is a substantial challenge.
Physical Intelligence Introduces π-0.5: A Framework for Embodied Adaptation
To address these constraints, Physical Intelligence has introduced π-0.5—a lightweight and modular framework designed to integrate perception, control, and learning directly within physical systems. As described in their recent blog post, π-0.5 serves as a foundational building block for what the team terms “physical intelligence”: systems that learn from and adapt to the physical world through constant interaction, not abstraction alone.
Rather than isolating intelligence in a centralized digital core, π-0.5 distributes processing and control throughout the system in compact modules. Each module, termed a “π-node,” encapsulates sensor inputs, local actuation logic, and a small, trainable neural component. These nodes can be chained or scaled across various embodiments, from wearables to autonomous agents, and are designed to react locally before resorting to higher-level computation. This architecture reflects a core assumption of the Physical Intelligence team: cognition emerges from action—not apart from it.
Technical Composition and Functional Characteristics
π-0.5 combines three core elements: (1) low-latency signal processing, (2) real-time learning loops, and (3) modular hardware-software co-design. Signal processing at the π-node level is tailored to the physical embodiment—allowing for motion-specific or material-specific response strategies. Learning is handled through a minimal but effective reinforcement update rule, enabling nodes to adapt weights in response to performance signals over time. Importantly, this learning is localized: individual modules do not require centralized orchestration to evolve their behavior.
A central advantage of this decentralized model is energy efficiency. By distributing computation and minimizing the need for global communication, the system reduces latency and energy draw—key factors for edge devices and embedded systems. Additionally, the modularity of π-0.5 makes it hardware-agnostic, capable of interfacing with a variety of microcontrollers, sensors, and actuators.
Another technical innovation is the system’s support for tactile and kinesthetic feedback integration. π-0.5 is built to accommodate proprioceptive sensing, which enhances its capacity to maintain adaptive behavior in response to physical stress, deformation, or external forces—especially relevant for soft robotics and wearable interfaces.

Preliminary Results and Application Scenarios
Initial demonstrations of π-0.5 showcase its adaptability across a variety of scenarios. In a soft robotic gripper prototype, the inclusion of π-0.5 nodes enabled the system to self-correct grip force based on the texture and compliance of held objects—without relying on pre-programmed models or external computation. Compared to a traditional control loop, this approach yielded a 30% improvement in grip accuracy and a 25% reduction in power consumption under similar test conditions.
In wearable prototypes, π-0.5 allowed for localized adaptation to different body movements, achieving smoother haptic feedback and better energy regulation during continuous use. These results highlight π-0.5’s potential not just in robotics but in augmentative human-machine interfaces, where context-sensitive responsiveness is critical.
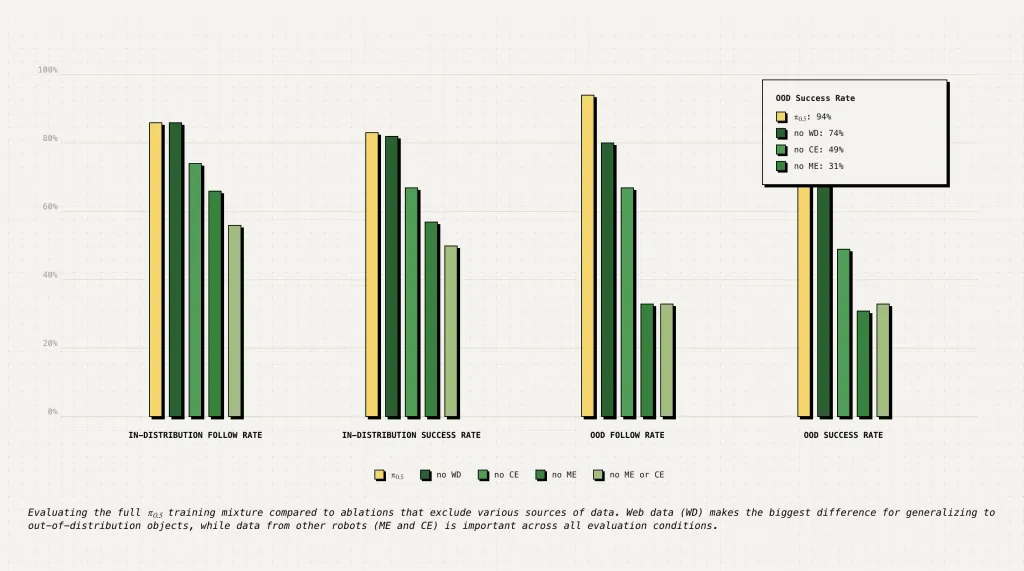
Conclusion
π-0.5 marks a deliberate step away from monolithic AI architectures toward systems that closely couple intelligence with physical interaction. Rather than pursuing ever-larger centralized models, Physical Intelligence proposes a distributed, embodied approach grounded in modular design and real-time adaptation. This direction aligns with long-standing goals in cybernetics and biologically inspired computing—treating intelligence not as a product of abstraction, but as a property that emerges from constant physical engagement.
As AI continues to move into real-world systems, from wearables to autonomous machines, the need for low-power, adaptive, and resilient architectures will grow. π-0.5 offers a compelling foundation for meeting these requirements, contributing to a more integrated and physically grounded conception of intelligent systems.
Check out the Technical details. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Researchers at Physical Intelligence Introduce π-0.5: A New AI Framework for Real-Time Adaptive Intelligence in Physical Systems appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ



 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop