Revisiting the Grokking Challenge
In recent years, the phenomenon of grokking—where deep learning models exhibit a delayed yet sudden transition from memorization to generalization—has prompted renewed investigation into training dynamics. Initially observed in small algorithmic tasks like modular arithmetic, grokking reveals that models can reach near-perfect training accuracy while validation performance remains poor for a prolonged period. Eventually, and often abruptly, the model begins to generalize. Understanding what governs this transition is important not just for interpretability, but also for optimizing training efficiency in deep networks. Prior studies have highlighted the role of weight decay and regularization. However, the specific influence of optimizers on this process has been underexplored.
Investigating Optimizer Effects on Grokking
This AI paper from Microsoft examines the impact of optimizer choice on grokking behavior. Specifically, it contrasts the performance of the widely adopted AdamW optimizer with Muon, a newer optimization algorithm that incorporates spectral norm constraints and second-order information. The study investigates whether these features enable Muon to expedite the generalization phase.
The experiments span seven algorithmic tasks—primarily modular arithmetic operations and parity classification—using a modern Transformer architecture. Each task is designed to reliably exhibit grokking under appropriate training conditions. The research also includes a comparative analysis of softmax variants (standard softmax, stablemax, and sparsemax) to evaluate whether output normalization plays a secondary role in modulating training dynamics. However, the core investigation centers on the optimizer.

Architectural and Optimization Design
The underlying model architecture adopts standard Transformer components, implemented in PyTorch. It includes multi-head self-attention, rotary positional embeddings (RoPE), RMS normalization, SiLU activations, and dropout-based regularization. Input tokens—numerical values or operators—are encoded through simple identity embeddings.
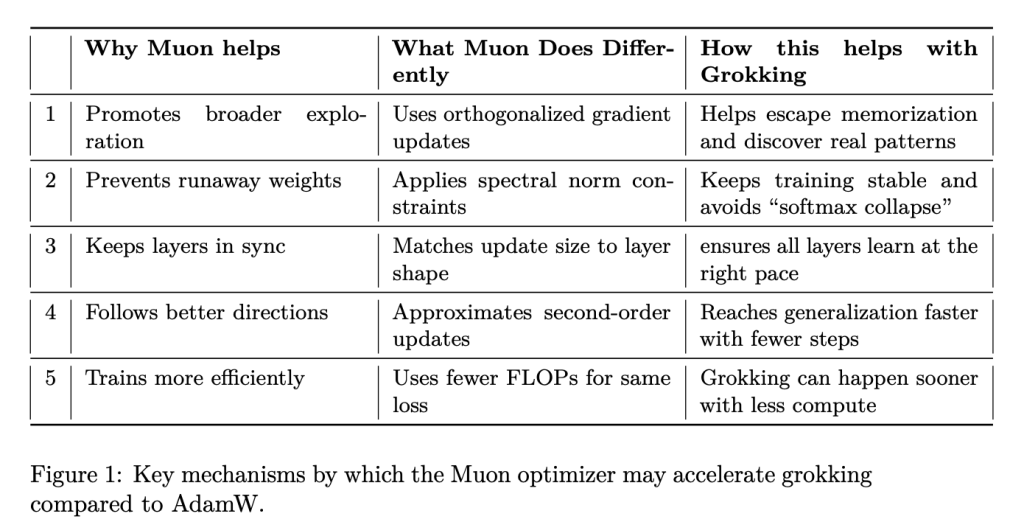
The key distinction lies in the optimizer behavior:
- AdamW, a baseline in contemporary deep learning workflows, uses adaptive learning rates with decoupled weight decay.
- Muon, in contrast, applies orthogonalized gradients, enforces spectral norm constraints to stabilize training, and approximates second-order curvature for more informative updates.
These mechanisms are intended to promote broader exploration during optimization, mitigate instability (e.g., “softmax collapse”), and synchronize learning progress across layers. Muon’s ability to regulate update magnitude in accordance with layer dimensions is particularly relevant in avoiding inefficient memorization pathways.
Three softmax configurations—Softmax, Stablemax, and Sparsemax—are included to assess whether numerical stability or sparsity of the output distribution influences grokking. This helps ensure that the observed effects stem primarily from optimizer dynamics rather than output activation nuances.
Empirical Evaluation and Results
The study’s empirical protocol is methodically designed. Each optimizer-softmax-task combination is evaluated across multiple seeds to ensure statistical robustness. Grokking is operationally defined as the first epoch where validation accuracy surpasses 95% following training accuracy stabilization.
The results indicate a consistent and statistically significant advantage for Muon. On average, Muon reaches the grokking threshold in 102.89 epochs, compared to 153.09 epochs for AdamW. This difference is not only numerically large but also statistically rigorous (t = 5.0175, p ≈ 6.33e−8). Additionally, Muon demonstrates a tighter distribution of grokking epochs across all conditions, suggesting more predictable training trajectories.
All tasks were conducted on NVIDIA H100 GPUs using a unified codebase and standardized configurations. Tasks include modular addition, multiplication, division, exponentiation, GCD, and a 10-bit parity task. Dataset sizes ranged from 1,024 to 9,409 examples, with training-validation splits adjusted per task to maintain consistency.
Conclusion
The findings provide strong evidence that optimizer geometry significantly influences the emergence of generalization in overparameterized models. By steering the optimization path through second-order-aware updates and spectral norm constraints, Muon appears to facilitate a more direct route toward discovering the underlying data structure, bypassing prolonged overfitting phases.
This study underscores the broader need to consider optimization strategy as a first-class factor in neural training design. While prior work emphasized data and regularization, these results suggest that optimizer architecture itself can play a pivotal role in shaping training dynamics.
Check out the Paper. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Muon Optimizer Significantly Accelerates Grokking in Transformers: Microsoft Researchers Explore Optimizer Influence on Delayed Generalization appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop