Integrating long-context capabilities with visual understanding significantly enhances the potential of VLMs, particularly in domains such as robotics, autonomous driving, and healthcare. Expanding the context size enables VLMs to process extended video and text sequences, thereby enhancing temporal resolution and performance in complex tasks, such as video comprehension. However, one major limitation is the quadratic complexity of attention mechanisms during the pre-fill phase, which results in high latency before autoregressive decoding begins. This delay, known as Time-to-First-Token, makes real-world deployment of long-context VLMs challenging. Various sparse attention methods, such as Sparse Transformer, Swin Transformer, and StreamingLLM, overlook the specific sparse patterns found in VLMs with mixed modalities, thereby limiting their efficiency and effectiveness.
Unlike text-only inputs, visual and video data in VLMs demonstrate unique spatiotemporal attention structures, forming grid-like patterns due to local correlations. In mixed-modality scenarios, clear boundaries exist between different modalities, leading to distinct attention behaviors that general sparse methods fail to capture. Recent advancements, such as MInference and dynamic sparse attention approaches, aim to improve inference efficiency by adapting attention patterns online. Yet, these techniques often fall short in handling the intricacies of mixed-modality inputs. While vision token compression and RNN-Transformer hybrids have been explored to reduce computational load, most of these methods focus on long-video and short-text pairings, neglecting the more complex dynamics of multiturn, mixed-modality interactions, which are increasingly important in practical applications.
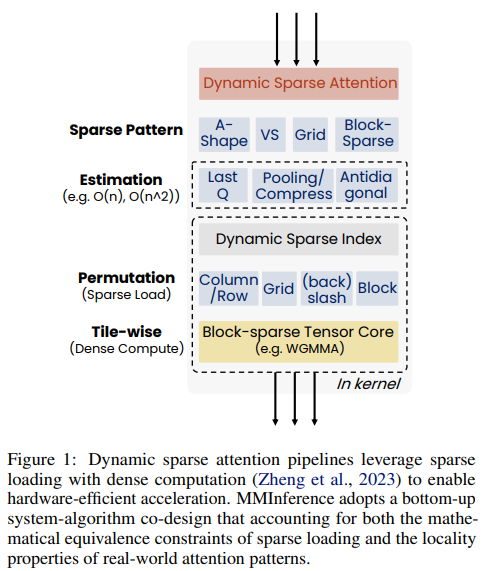
Researchers from the University of Surrey and Microsoft have introduced MMInference, a dynamic, sparse attention method designed to accelerate the pre-filling stage of long-context VLMs. By identifying grid-like sparsity patterns in video inputs and distinct modality boundaries, MMInference applies permutation-based strategies to optimize attention computation. It dynamically constructs sparse distributions for each input and utilizes custom GPU kernels for enhanced efficiency, all without requiring modifications to existing models. Tested on benchmarks like Video QA, Captioning, and Vision-NIAH, MMInference achieved up to 8.3× speedup at 1M tokens, outperforming previous methods while maintaining high accuracy across multiple state-of-the-art VLMs.
MMInference is a framework designed to speed up the pre-filling phase of long-context vision-language models by leveraging modality-aware sparse attention. It integrates three key components: (1) intra-modality sparse patterns like Grid, A-shape, and Vertical-Slash attention; (2) cross-modality patterns such as Q-Boundary and 2D-Boundary; and (3) a modality-aware sparse attention search algorithm. Instead of dense computation, it uses dynamic sparse attention with optimized GPU kernels and efficient tensor handling. The framework dynamically identifies attention patterns and permutes tensors based on modality, enabling efficient handling of multi-modal inputs and reducing computational overhead while maintaining strong performance.
The study evaluates MMInference’s performance and efficiency on long-video tasks, including captioning, question answering, and retrieval in both unimodal and mixed-modality settings. Experiments were conducted using state-of-the-art models, such as Llava-Video and LongVILA, with comparisons against several sparse attention baselines. Results show that MMInference achieves near full-attention performance while being more computationally efficient. It performs particularly well in the newly introduced Mixed-Modality Needle in a Haystack (MM-NIAH) task by leveraging inter-modality sparse patterns. Additionally, MMInference demonstrates significant speedups in end-to-end latency and maintains robustness across varying context lengths and input types.
In conclusion, MMInference is a modality-aware sparse attention technique designed to accelerate long-context VLMs without compromising accuracy. It employs a permutation-based grid attention pattern tailored for the spatial-temporal locality of video inputs, along with specialized handling for mixed-modality boundaries. A search algorithm identifies optimal sparse patterns per attention head, dynamically adapting to the input. The method integrates directly into current VLM pipelines without requiring model changes or fine-tuning. With optimized GPU kernels, MMInference achieves up to 8.3× acceleration during the pre-filling stage at 1M tokens across various tasks, including video QA, captioning, and mixed-modality benchmarks, while retaining full-attention performance.
Check out the Paper and Code. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Microsoft Research Introduces MMInference to Accelerate Pre-filling for Long-Context Vision-Language Models appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop