LLM-based multi-agent systems characterized by planning, reasoning, tool use, and memory capabilities form the foundation of applications like chatbots, code generation, mathematics, and robotics. However, these systems face significant challenges as they are manually designed, leading to high human resource costs and limited scalability. Graph-based methods have attempted to automate workflow designs by formulating workflows as networks, but their structural complexity restricts scalability. State-of-the-art approaches represent multi-agent systems as programming code and use advanced LLMs as meta-agents to optimize workflows, but focus on task-level solutions that generate single task-specific systems. This one-size-fits-all approach lacks the capability for automatic adaptation to individual user queries.
LLM-based multi-agent systems are the foundation for various real-world applications, including code intelligence, computer use, and deep research. These systems feature LLM-based agents equipped with planning capabilities, database access, and tool function invocation that collaborate to achieve promising performance. Early approaches focused on optimizing prompts or hyperparameters through evolution algorithms to automate agent profiling. ADAS introduced code representation for agents and workflows with a meta-agent to generate workflows. Moreover, OpenAI has advanced reasoning in LLMs by developing the o1 model. Models like QwQ, QvQ, DeepSeek, and Kimi have followed suit, developing o1-like reasoning architectures. OpenAI’s o3 model achieves promising results on the ARG-AGI benchmark.
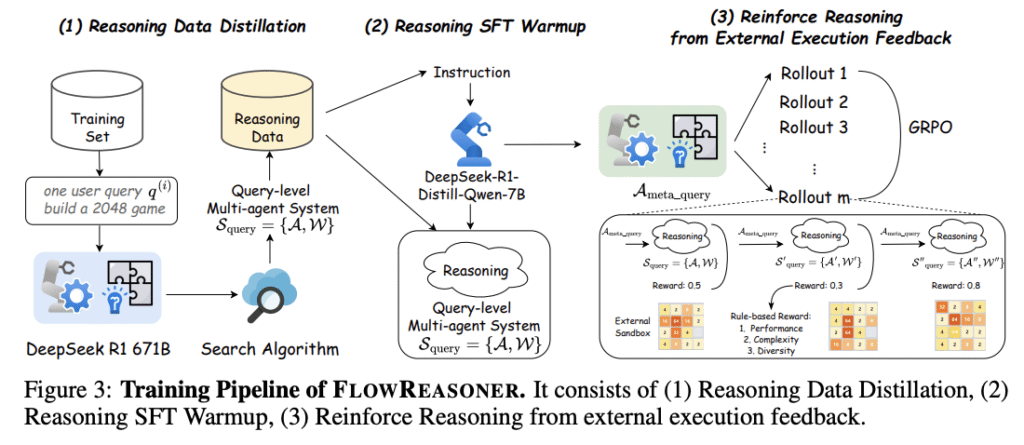
Researchers from the Sea AI Lab, Singapore, the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National University of Singapore, and Shanghai Jiao Tong University have proposed FlowReasoner, a query-level meta-agent designed to automate the creation of query-level multi-agent systems, generating one customized system per user query. The researchers distilled DeepSeek R1 to supply FlowReasoner with the fundamental reasoning capabilities needed to create multi-agent systems, and then enhanced it through reinforcement learning with external execution feedback. A multi-purpose reward mechanism is developed to optimize training across three critical dimensions: performance, complexity, and efficiency. This enables FlowReasoner to generate personalized multi-agent systems through deliberative reasoning for each unique user query.
The researchers select three datasets: BigCodeBench for engineering-oriented tasks, HumanEval, and MBPP for algorithmic challenges for detailed evaluation across diverse code generation scenarios. FlowReasoner is evaluated against three categories of baselines:
- Single-model direct invocation using standalone LLMs
- Manually designed workflows including Self-Refine, LLM-Debate, and LLM-Blender with human-crafted reasoning strategies
- Automated workflow optimization methods like Aflow, ADAS, and MaAS that construct workflows through search or optimization.
Both o1-mini and GPT-4o-mini are used as worker models for manually designed workflows. FlowReasoner is implemented with two variants of DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen (7B and 14B parameters) using o1-mini as the worker model.
FlowReasoner-14B outperforms all competing approaches, achieving an overall improvement of 5 percentage points compared to the strongest baseline, MaAS. It exceeds the performance of its underlying worker model, o1-mini, by a substantial margin of 10%. These results show the effectiveness of the workflow-based reasoning framework in enhancing code generation accuracy. To evaluate generalization capabilities, experiments are conducted replacing the o1-mini worker with models like Qwen2.5-Coder, Claude, and GPT-4o-mini, while keeping the meta-agent fixed as either FLOWREASONER-7B or FLOWREASONER-14B. FLOWREASONER exhibits notable transferability, maintaining consistent performance across different worker models on the same tasks.
In this paper, researchers present FlowReasoner, a query-level meta-agent designed to automate the creation of personalized multi-agent systems for individual user queries. FlowReasoner utilizes external execution feedback and reinforcement learning with multi-purpose rewards focusing on performance, complexity, and efficiency to generate optimized workflows without relying on complex search algorithms or carefully designed search sets. This approach reduces human resource costs while enhancing scalability by enabling more adaptive and efficient multi-agent systems that dynamically optimize their structure based on specific user queries rather than relying on fixed workflows for entire task categories.
Check out the Paper and GitHub Page. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Researchers from Sea AI Lab, UCAS, NUS, and SJTU Introduce FlowReasoner: a Query-Level Meta-Agent for Personalized System Generation appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop