The development of agentic systems—LLMs embedded within scaffolds capable of tool use and autonomous decision-making—has made significant progress. Yet, most implementations today rely on fixed, hand-crafted orchestration strategies. These designs are inherently constrained, limiting the agent’s adaptability to new tasks and environments. As models grow in capability, the rigidity of their execution frameworks becomes a bottleneck, especially in domains such as software engineering where the task complexity and variability demand a more flexible system.
In response, researchers from the University of Bristol and iGent AI have introduced SICA (Self-Improving Coding Agent)—a novel agent architecture designed to iteratively enhance its own performance by modifying its underlying code. Unlike prior methods, such as ADAS, which split responsibilities between a meta-agent and a target-agent, SICA unifies these roles. The same agent that performs the task is also responsible for evaluating past performance, identifying shortcomings, and updating its own implementation. This integration allows for a continuous loop of self-directed improvement without external intervention.

Architecture and Mechanism of Self-Improvement
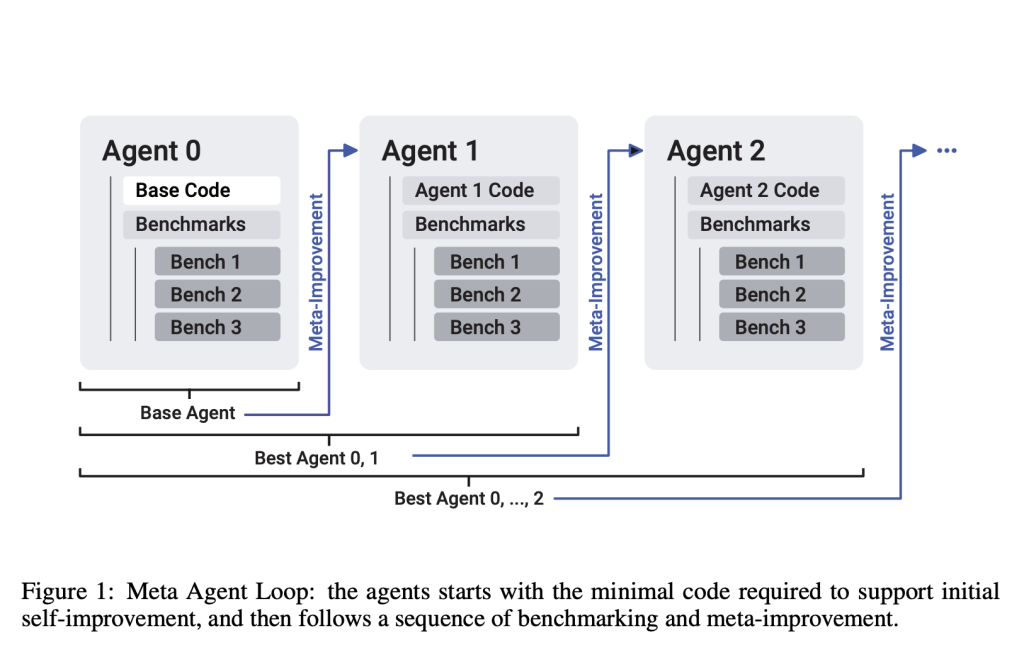
SICA is built upon a minimal, extensible base agent equipped with tools to manipulate its codebase, navigate directories, execute shell commands, and invoke sub-agents. Its architecture follows a loop: evaluate, select, revise. At each iteration, the agent benchmarks its own performance on predefined tasks, stores results, and selects the most effective prior version to serve as the basis for further improvement.
The agent evaluates performance using a utility function that combines accuracy, time, and cost metrics. Key components include:
- Sub-agent structure for decomposing problems and managing context within LLM constraints.
- Asynchronous oversight, a monitoring LLM thread that ensures the agent remains on-task and halts execution in cases of non-progress or divergence.
- Self-editing capabilities, with tools such as SmartEditor, AST-based symbol locators, and diff summarizers that enable precise modifications to the agent’s behavior.
This structure allows the agent to conduct controlled experiments on its own design and deploy updates that demonstrably improve outcomes.
Empirical Evaluation
The researchers evaluated SICA on several code-related benchmarks, including a subset of SWE Bench Verified, LiveCodeBench, and synthetic tasks focused on file editing and symbol location. Results indicate measurable gains across iterations. For instance, accuracy on SWE Bench Verified increased from 17% to 53%, and file editing performance improved from 82% to 94%.
These improvements were not limited to benchmark scores. The agent also optimized execution latency and resource efficiency, reducing average cost and time per task. Notably, improvements were not the result of weight updates to the underlying LLM but were achieved through changes in tool orchestration, file management strategies, and problem decomposition heuristics.
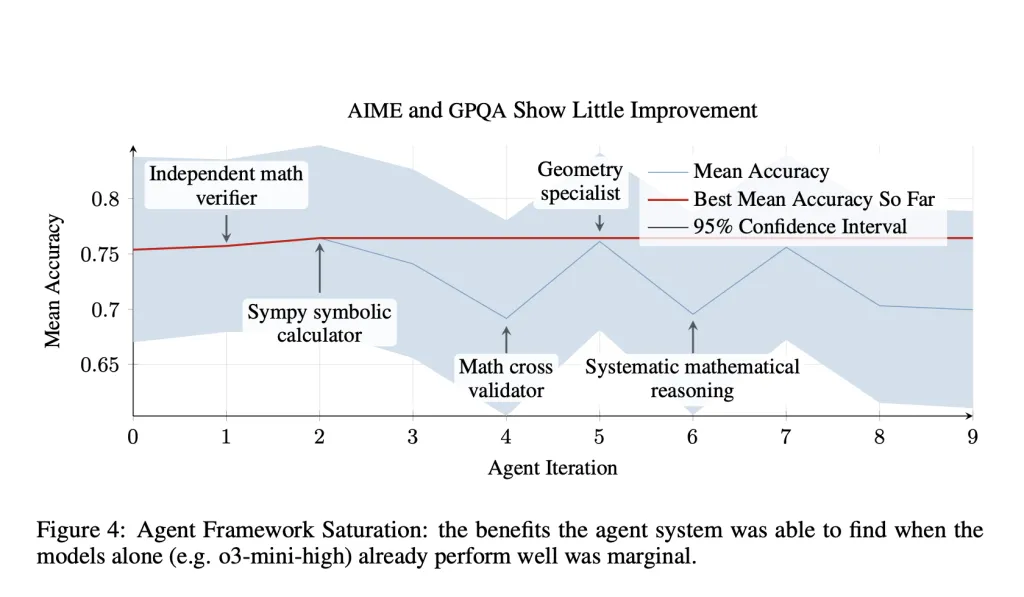
However, gains were less pronounced on reasoning-dominant tasks such as AIME and GPQA. In these cases, the performance of the base LLM (e.g., o3-mini) already approached the task ceiling, limiting the marginal benefit of additional scaffolding. Moreover, introducing certain tool-based reasoning steps appeared to disrupt rather than enhance the performance of pretrained reasoning models, suggesting a need for more integrated co-training between agent logic and model behavior.
Conclusion
The SICA framework illustrates a concrete path toward autonomous improvement in agent systems. By consolidating execution and self-editing within a single agent, the system avoids many pitfalls of manual design and enables iterative refinement driven by empirical feedback. The results show that this approach is viable, particularly in domains with long-horizon, tool-mediated tasks such as software engineering.
While there are clear boundaries to the effectiveness of scaffold-only improvements—especially for tasks dominated by pure reasoning—the research establishes a foundation for future work in hybrid optimization, where both the model and the agent design evolve jointly. SICA also introduces practical considerations for safety and observability in self-improving systems, using LLM-based overseers and structured execution traces to ensure transparency and control.
Check out the Paper and GitHub Page. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Can Coding Agents Improve Themselves? Researchers from University of Bristol and iGent AI Propose SICA (Self-Improving Coding Agent) that Iteratively Enhances Its Own Code and Performance appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop