MCP-Use is an open-source library that lets you connect any LLM to any MCP server, giving your agents tool access like web browsing, file operations, and more — all without relying on closed-source clients. In this tutorial, we’ll use langchain-groq and MCP-Use’s built-in conversation memory to build a simple chatbot that can interact with tools via MCP.
Step 1: Setting Up the Environment
Installing uv package manager
We will first set up our environment and start with installing the uv package manager. For Mac or Linux:
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh For Windows (PowerShell):
powershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex"Creating a new directory and activating a virtual environment
We will then create a new project directory and initialize it with uv
uv init mcp-use-demo
cd mcp-use-demoWe can now create and activate a virtual environment. For Mac or Linux:
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activateFor Windows:
uv venv
.venvScriptsactivateInstalling Python dependencies
We will now install the required dependencies
uv add mcp-use langchain-groq python-dotenvStep 2: Setting Up the Environment Variables
Groq API Key
To use Groq’s LLMs:
- Visit Groq Console and generate an API key.
- Create a .env file in your project directory and add the following line:
GROQ_API_KEY=<YOUR_API_KEY>Replace <YOUR_API_KEY> with the key you just generated.
Brave Search API Key
This tutorial uses the Brave Search MCP Server.
- Get your Brave Search API key from: Brave Search API
- Create a file named mcp.json in the project root with the following content:
{
"mcpServers": {
"brave-search": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@modelcontextprotocol/server-brave-search"
],
"env": {
"BRAVE_API_KEY": "<YOUR_BRAVE_SEARCH_API>"
}
}
}
}Replace <YOUR_BRAVE_SEARCH_API> with your actual Brave API key.
Node JS
Some MCP servers (including Brave Search) require npx, which comes with Node.js.
- Download the latest version of Node.js from nodejs.org
- Run the installer.
- Leave all settings as default and complete the installation
Using other servers
If you’d like to use a different MCP server, simply replace the contents of mcp.json with the configuration for that server.
Step 3: Implementing the chatbot and integrating the MCP server
Create an app.py file in the directory and add the following content:
Importing the libraries
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from langchain_groq import ChatGroq
from mcp_use import MCPAgent, MCPClient
import os
import sys
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=ResourceWarning)This section loads environment variables and imports required modules for LangChain, MCP-Use, and Groq. It also suppresses ResourceWarning for cleaner output.
Setting up the chatbot
async def run_chatbot():
""" Running a chat using MCPAgent's built in conversation memory """
load_dotenv()
os.environ["GROQ_API_KEY"] = os.getenv("GROQ_API_KEY")
configFile = "mcp.json"
print("Starting chatbot...")
# Creating MCP client and LLM instance
client = MCPClient.from_config_file(configFile)
llm = ChatGroq(model="llama-3.1-8b-instant")
# Creating an agent with memory enabled
agent = MCPAgent(
llm=llm,
client=client,
max_steps=15,
memory_enabled=True,
verbose=False
)This section loads the Groq API key from the .env file and initializes the MCP client using the configuration provided in mcp.json. It then sets up the LangChain Groq LLM and creates a memory-enabled agent to handle conversations.
Implementing the chatbot
# Add this in the run_chatbot function
print("n-----Interactive MCP Chat----")
print("Type 'exit' or 'quit' to end the conversation")
print("Type 'clear' to clear conversation history")
try:
while True:
user_input = input("nYou: ")
if user_input.lower() in ["exit", "quit"]:
print("Ending conversation....")
break
if user_input.lower() == "clear":
agent.clear_conversation_history()
print("Conversation history cleared....")
continue
print("nAssistant: ", end="", flush=True)
try:
response = await agent.run(user_input)
print(response)
except Exception as e:
print(f"nError: {e}")
finally:
if client and client.sessions:
await client.close_all_sessions()This section enables interactive chatting, allowing the user to input queries and receive responses from the assistant. It also supports clearing the chat history when requested. The assistant’s responses are displayed in real-time, and the code ensures that all MCP sessions are closed cleanly when the conversation ends or is interrupted.
Running the app
if __name__ == "__main__":
import asyncio
try:
asyncio.run(run_chatbot())
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Session interrupted. Goodbye!")
finally:
sys.stderr = open(os.devnull, "w")This section runs the asynchronous chatbot loop, managing continuous interaction with the user. It also handles keyboard interruptions gracefully, ensuring the program exits without errors when the user terminates the session.
You can find the entire code here
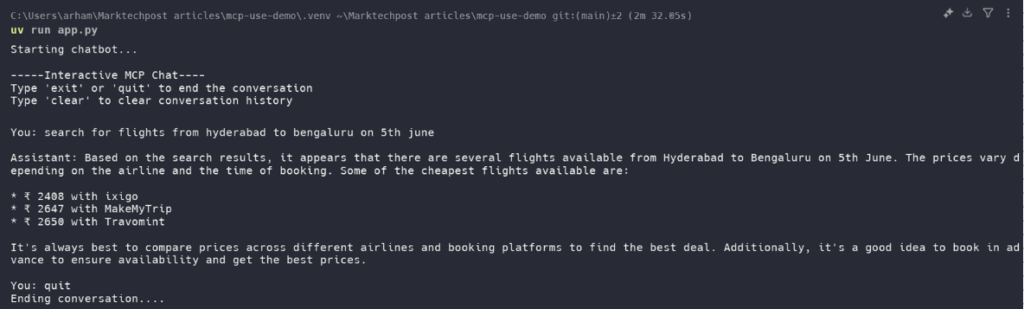
Step 4: Running the app
To run the app, run the following command
uv run app.pyThis will start the app, and you can interact with the chatbot and use the server for the session
The post Implementing an LLM Agent with Tool Access Using MCP-Use appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ