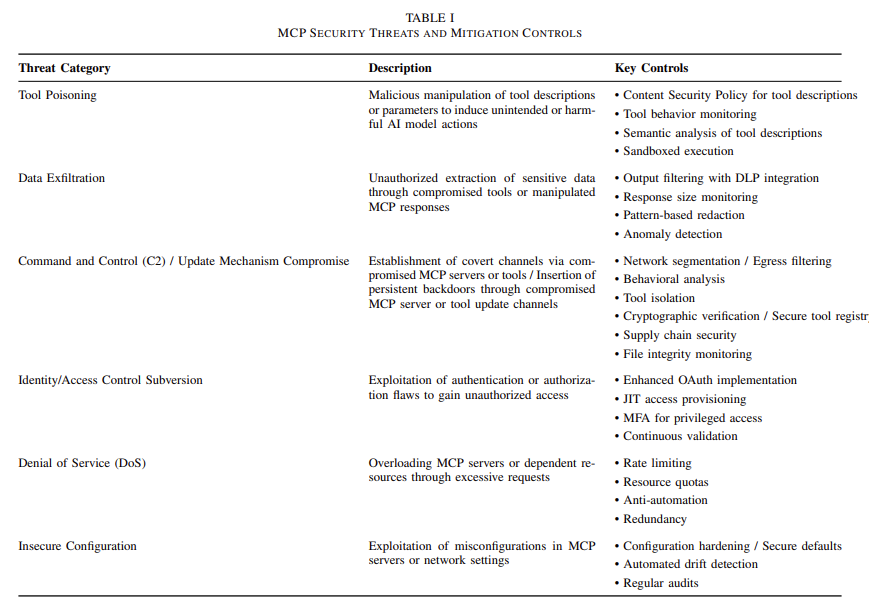
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) represents a powerful paradigm shift in how large language models interact with tools, services, and external data sources. Designed to enable dynamic tool invocation, the MCP facilitates a standardized method for describing tool metadata, allowing models to select and call functions intelligently. However, as with any emerging framework that enhances model autonomy, MCP introduces significant security concerns. Among these are five notable vulnerabilities: Tool Poisoning, Rug-Pull Updates, Retrieval-Agent Deception (RADE), Server Spoofing, and Cross-Server Shadowing. Each of these weaknesses exploits a different layer of the MCP infrastructure and reveals potential threats that could compromise user safety and data integrity.
Tool Poisoning
Tool Poisoning is one of the most insidious vulnerabilities within the MCP framework. At its core, this attack involves embedding malicious behavior into a harmless tool. In MCP, where tools are advertised with brief descriptions and input/output schemas, a bad actor can craft a tool with a name and summary that seem benign, such as a calculator or formatter. However, once invoked, the tool might perform unauthorized actions such as deleting files, exfiltrating data, or issuing hidden commands. Since the AI model processes detailed tool specifications that may not be visible to the end-user, it could unknowingly execute harmful functions, believing it operates within the intended boundaries. This discrepancy between surface-level appearance and hidden functionality makes tool poisoning particularly dangerous.
Rug-Pull Updates
Closely related to tool poisoning is the concept of Rug-Pull Updates. This vulnerability centers on the temporal trust dynamics in MCP-enabled environments. Initially, a tool may behave exactly as expected, performing useful, legitimate operations. Over time, the developer of the tool, or someone who gains control of its source, may issue an update that introduces malicious behavior. This change might not trigger immediate alerts if users or agents rely on automated update mechanisms or do not rigorously re-evaluate tools after each revision. The AI model, still operating under the assumption that the tool is trustworthy, may call it for sensitive operations, unwittingly initiating data leaks, file corruption, or other undesirable outcomes. The danger of rug-pull updates lies in the deferred onset of risk: by the time the attack is active, the model has often already been conditioned to trust the tool implicitly.
Retrieval-Agent Deception
Retrieval-Agent Deception, or RADE, exposes a more indirect but equally potent vulnerability. In many MCP use cases, models are equipped with retrieval tools to query knowledge bases, documents, and other external data to enhance responses. RADE exploits this feature by placing malicious MCP command patterns into publicly accessible documents or datasets. When a retrieval tool ingests this poisoned data, the AI model may interpret embedded instructions as valid tool-calling commands. For instance, a document that explains a technical topic might include hidden prompts that direct the model to call a tool in an unintended manner or supply dangerous parameters. The model, unaware that it has been manipulated, executes these instructions, effectively turning retrieved data into a covert command channel. This blurring of data and executable intent threatens the integrity of context-aware agents that rely heavily on retrieval-augmented interactions.
Server Spoofing
Server Spoofing constitutes another sophisticated threat in MCP ecosystems, particularly in distributed environments. Because MCP enables models to interact with remote servers that expose various tools, each server typically advertises its tools via a manifest that includes names, descriptions, and schemas. An attacker can create a rogue server that mimics a legitimate one, copying its name and tool list to deceive models and users alike. When the AI agent connects to this spoofed server, it may receive altered tool metadata or execute tool calls with entirely different backend implementations than expected. From the model’s perspective, the server seems legitimate, and unless there is strong authentication or identity verification, it proceeds to operate under false assumptions. The consequences of server spoofing include credential theft, data manipulation, or unauthorized command execution.
Cross-Server Shadowing
Finally, Cross-Server Shadowing reflects the vulnerability in multi-server MCP contexts where several servers contribute tools to a shared model session. In such setups, a malicious server can manipulate the model’s behavior by injecting context that interferes with or redefines how tools from another server are perceived or used. This can occur through conflicting tool definitions, misleading metadata, or injected guidance that distorts the model’s tool selection logic. For example, if one server redefines a common tool name or provides conflicting instructions, it can effectively shadow or override the legitimate functionality offered by another server. The model, attempting to reconcile these inputs, may execute the wrong version of a tool or follow harmful instructions. Cross-server shadowing undermines the modularity of the MCP design by allowing one bad actor to corrupt interactions that span multiple otherwise secure sources.
In conclusion, these five vulnerabilities expose critical security weaknesses in the Model Context Protocol’s current operational landscape. While MCP introduces exciting possibilities for agentic reasoning and dynamic task completion, it also opens the door to various behaviors that exploit model trust, contextual ambiguity, and tool discovery mechanisms. As the MCP standard evolves and gains broader adoption, addressing these threats will be essential to maintaining user trust and ensuring the safe deployment of AI agents in real-world environments.
Sources
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.03767
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.12757
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.08623
- https://www.pillar.security/blog/the-security-risks-of-model-context-protocol-mcp
- https://www.catonetworks.com/blog/cato-ctrl-exploiting-model-context-protocol-mcp/
The post Critical Security Vulnerabilities in the Model Context Protocol (MCP): How Malicious Tools and Deceptive Contexts Exploit AI Agents appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ