Recent advances in long-context (LC) modeling have unlocked new capabilities for LLMs and large vision-language models (LVLMs). Long-context vision–language models (LCVLMs) show an important step forward by enabling LVLMs to process hundreds of images and thousands of interleaved text tokens in a single forward pass. However, the development of effective evaluation benchmarks lags. It is still unclear how well current LCVLMs perform in long-context settings, what tasks they struggle with, and how robust they are to input length variation. Current benchmarks face the following problem: (a) Limited coverage of downstream tasks, (b) Insufficient coverage of image types, (c) Lack of context length control, and (d) Single context length.
Various techniques have extended context windows for LVLMs, including longer pre-training lengths, position extrapolation, and efficient architectures. Models like Gemini-2.5 and Qwen2.5-VL have adopted these approaches alongside vision token compression methods to accommodate longer sequences. For evaluation, the Needle-in-a-Haystack task became a standard benchmark for testing LC ability by inserting information at specific depths within long texts. However, existing vision-language benchmarks remain limited, focusing only on NIAH variants or long-document VQA tasks. Even MileBench contains short-context tasks with an average length of only 9K tokens, failing to evaluate true LC capabilities across diverse vision-language applications.
Researchers from HKUST, Tencent AI Seattle Lab, University of Edinburgh, Miniml.AI, and NVIDIA AI Technology Center have proposed MMLONGBENCH, the first comprehensive benchmark for evaluating LCVLMs. It comprises 13,331 examples spanning five downstream task categories, including Visual RAG and Many-Shot ICL, covering natural and synthetic image types. All examples are standardized across five input lengths from 8K to 128K tokens using a cross-modal tokenization scheme combining vision patches and text tokens. Through benchmarking 46 closed-source and open-source models, the research reveals that single-task performance poorly predicts overall LC capability, both model types struggle with LC tasks, and stronger reasoning models show better LC performance.
Researchers construct LC by inserting gold passages containing answers among large sets of distracting passages retrieved from Wikipedia. For ViQuAE, gold passages from KILT are used, while InfoSeek uses lead sections from Wikipedia entity pages. Further, Wikipedia pages are split into 100-word passages, and retrieved distractors are added until reaching desired input lengths. Many-shot in-context learning tasks utilize four diverse image classification datasets: Stanford Cars, Food101, SUN397, and iNat2021, accommodating 500 images within 128K context windows. Cross-modal token counting combines text tokens using the Llama2 tokenizer with visual tokens processed through 14×14 patches and 2×2 pixel unshuffle compression, ensuring compatibility with modern LVLMs for evaluation.
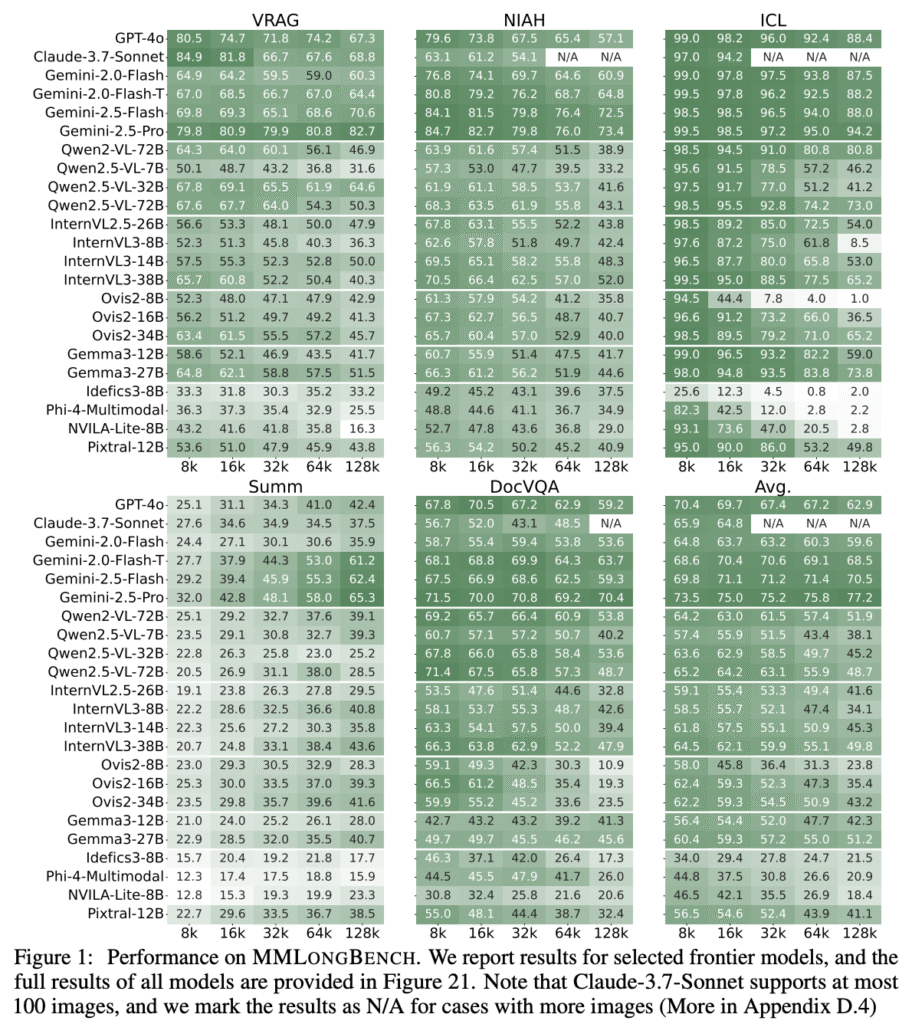
The evaluation on MMLONGBENCH across tasks and context Lengths shows that all models struggle, but closed-source models perform better. For the longest input length of 128K, all models struggle with long-context vision-language tasks, with GPT-4o achieving only 62.9 average performance. Gemini-2.5-Pro became the strongest performer, outperforming open-source models by 20 points except on ICL tasks. Further, Ovis2-34B model achieves a score of 41.6 on summarization, similar to GPT-4o (42.4). Qwen2.5-VL-32B achieves a SubEM score of 64.6 on VRAG, even better than Gemini-2.0-Flash. Models show generalization capabilities beyond their training context lengths, with Qwen2-VL-72B achieving a 51.9 average score at 128K despite a 32K training window.
In conclusion, researchers introduced MMLONGBENCH, the first comprehensive benchmark for evaluating LCVLMs across diverse downstream tasks. It provides a rigorous foundation for diagnosing frontier model capabilities by covering five distinct task categories with unified cross-modal token counting and standardized context lengths. The evaluation of 46 models demonstrates that single-task performance unreliably predicts overall long-context ability, and frontier models face significant challenges in OCR accuracy and cross-modal retrieval. MMLONGBENCH is a standard evaluation framework to drive future research toward more efficient vision-language token encodings, robust position-extrapolation schemes, and improved multi-modal retrieval and reasoning capabilities.
Check out the Paper and GitHub Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 95k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post Researchers Introduce MMLONGBENCH: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Long-Context Vision-Language Models appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ