Web automation agents have become a growing focus in artificial intelligence, particularly due to their ability to execute human-like actions in digital environments. These agents interact with websites via Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs), mimicking human behaviors such as clicking, typing, and navigating across web pages. This approach bypasses the need for dedicated Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), which are often unavailable or limited in many web applications. Instead, these agents can operate universally across web domains, making them flexible tools for a broad range of tasks. The evolution of large language models (LLMs) has enabled these agents to not only interpret web content but also reason, plan, and act with increasing sophistication. As their abilities grow, so too does the need to evaluate them on more than just simple browsing tasks. Benchmarks that once sufficed for early models are no longer capable of measuring the full extent of modern agents’ capabilities.
As these web agents progress, a pressing issue arises: their competence in handling mundane, memory-intensive, and multi-step digital chores remains insufficiently measured. Many tasks that humans perform on websites, such as retrieving data from different pages, performing calculations based on previous inputs, or applying complex rules, require significant cognitive effort. These are not merely navigation challenges; they test memory, logic, and long-term planning. Yet most benchmarks focus on simplified scenarios, failing to reflect the types of digital chores people often prefer to avoid. Furthermore, the limitations in these benchmarks become more apparent as agents improve their performance. Ambiguities in task instructions or inconsistencies in expected outputs begin to skew evaluations. When agents generate reasonable but slightly divergent answers, they are penalized incorrectly due to vague task definitions. Such flaws make it difficult to distinguish between true model limitations and benchmark shortcomings.
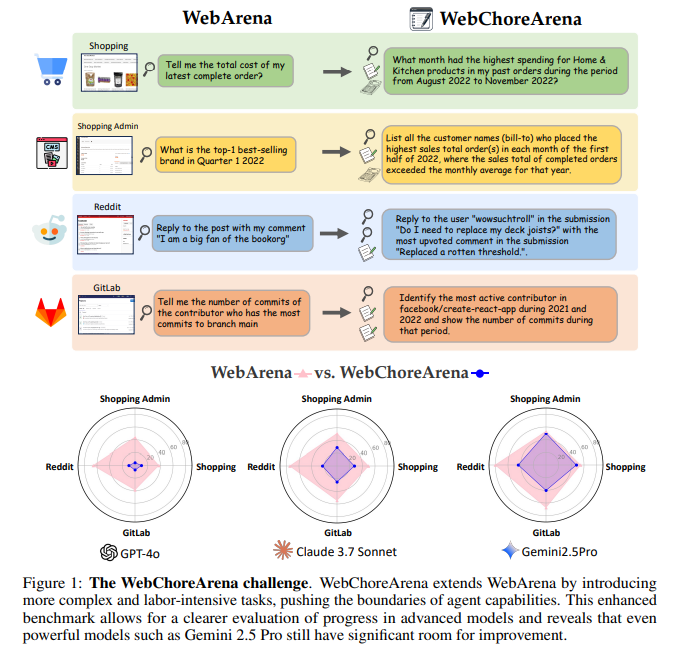
Previous efforts to evaluate web agents have focused on benchmarks such as WebArena. WebArena gained widespread adoption due to its reproducibility and ability to simulate real-world websites, including Reddit, GitLab, and E-Commerce Platforms. It offered over 800 tasks designed to test an agent’s ability to complete web-based goals within these environments. However, these tasks mostly focused on general browsing and did not adequately challenge more advanced agents. Other benchmarks, such as Mind2Web, GAIA, and MMIn, contributed by exploring real web tasks or platform-specific environments like ServiceNow, but each came with trade-offs. Some lacked interactivity, others did not support reproducibility, and some were too narrowly scoped. These limitations created a gap in measuring agent progress in areas that require complex decision-making, long-term memory, and accurate data processing across multiple webpages.
Researchers from the University of Tokyo introduced WebChoreArena. This expanded framework builds upon the structure of WebArena but significantly increases task difficulty and complexity. WebChoreArena features a total of 532 newly curated tasks, distributed across the same four simulated websites. These tasks are designed to be more demanding, reflecting scenarios where agents must engage in tasks like data aggregation, memory recall, and multi-step reasoning. Importantly, the benchmark was constructed to ensure full reproducibility and standardization, enabling fair comparisons between agents and avoiding the ambiguities found in earlier tools. The inclusion of diverse task types and input modalities helps simulate realistic web usage and evaluates agents on a more practical and challenging scale.
WebChoreArena categorizes its tasks into four main types. One hundred seventeen tasks fall under Massive Memory, requiring agents to extract and remember large volumes of information, such as compiling all customer names linked to high-value transactions. Calculation tasks, which include 132 entries, involve arithmetic operations like identifying the highest spending months based on multiple data points. Long-Term Memory tasks number 127 and test the agent’s ability to connect information across various pages, such as retrieving pricing rules from one site and applying them on another. An additional 65 tasks are categorized as ‘Others’, including operations such as assigning labels in GitLab that do not fit traditional task formats. Each task specifies its input modality, with 451 tasks solvable with any observation type, 69 requiring only textual input, and 12 dependent exclusively on image inputs.
In evaluating the benchmark, the researchers used three prominent large language models: GPT-4o, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, and Gemini 2.5 Pro. These were tested in conjunction with two advanced web agents, AgentOccam and BrowserGym. The results highlighted the increased difficulty of WebChoreArena compared to previous benchmarks. GPT-4o, which had achieved 42.8% accuracy on WebArena, managed only 6.8% on WebChoreArena. Claude 3.7 Sonnet and Gemini 2.5 Pro performed better, with Gemini reaching a peak accuracy of 44.9%. Despite being the top performer, this result still reflected significant gaps in capability when dealing with the more complex tasks of WebChoreArena. The benchmark also proved more sensitive in detecting performance differences between models, making it a valuable tool for benchmarking ongoing advances in web agent technologies.
Several Key Takeaways from the research include:
- WebChoreArena includes 532 tasks: 117 Massive Memory, 132 Calculation, 127 Long-Term Memory, and 65 Others.
- Tasks are distributed across Shopping (117), Shopping Admin (132), Reddit (91), GitLab (127), and 65 Cross-site scenarios.
- Input types: 451 tasks are solvable with any input, 69 require textual input, and 12 need image input.
- GPT-4o scored only 6.8% on WebChoreArena compared to 42.8% on WebArena.
- Gemini 2.5 Pro achieved the highest score at 44.9%, indicating current limitations in handling complex tasks.
- WebChoreArena provides a clearer performance gradient between models than WebArena, enhancing benchmarking value.
- A total of 117 task templates were used to ensure diversity and reproducibility across roughly 4.5 instances per template.
- The benchmark demanded over 300 hours of annotation and refinement, reflecting its rigorous construction.
- Evaluations utilize string matching, URL matching, and HTML structure comparisons to assess accuracy.
In conclusion, this research highlights the disparity between general browsing proficiency and the higher-order cognitive abilities necessary for web-based tasks. The newly introduced WebChoreArena stands as a robust and detailed benchmark designed specifically to push web agents into territories where they must rely on reasoning, memory, and logic. It replaces ambiguity with standardization, and its tasks mimic the digital drudgery that agents must learn to handle if they are to become truly useful in automating real-world activities.
Check out the Paper, GitHub Page and Project Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project.
 Did you know? Marktechpost is the fastest-growing AI media platform—trusted by over 1 million monthly readers. Book a strategy call to discuss your campaign goals. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 95k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
Did you know? Marktechpost is the fastest-growing AI media platform—trusted by over 1 million monthly readers. Book a strategy call to discuss your campaign goals. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 95k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post From Clicking to Reasoning: WebChoreArena Benchmark Challenges Agents with Memory-Heavy and Multi-Page Tasks appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ