When every click behaves exactly as a product owner expects, it is tempting to believe the release is rock‑solid. However, real users and real attackers rarely follow the script. They mistype email addresses, paste emojis into form fields, lose network connectivity halfway through checkout, or probe your APIs with malformed JSON. Negative testing exists precisely to prepare software for this chaos. Nevertheless, many teams treat negative scenarios in testing as optional when sprint capacity is tight. Unfortunately, the numbers say otherwise. Gartner puts the global average cost of a minute of critical‑system downtime at US $5,600, while Ponemon’s 2024 report pegs the average data‑breach bill at US $4.45 million. Identifying validation gaps, unhandled exceptions, and security loopholes before production not only protects revenue and brand reputation; it also accelerates release cycles because engineers have fewer late‑stage fires to fight.
In this comprehensive guide, you will discover:
1. The concrete difference between negative and positive testing.
2. Six business‑driven reasons negative scenarios matter.
3. Proven techniques from exploratory testing to JWT forgery that surface hidden defects.
4. Practical best practices that weave negative tests into your CI/CD flow.
5. A real‑world banking app incident that underscores the ROI.
6. How our methodology compares with other leading QA providers, so you can choose with confidence.
By the end, you will own a playbook that elevates quality, strengthens security, and most importantly wins stakeholder trust.
- Negative vs. Positive Testing
- Why Negative Scenarios Matter
- Key Techniques for Designing Negative Tests
- Best Practices for Planning and Execution
- Sample Negative Test Edge Cases
- Common Pitfalls and How to Dodge Them
- From Theory to Practice: A Concise Checklist
Related Blogs
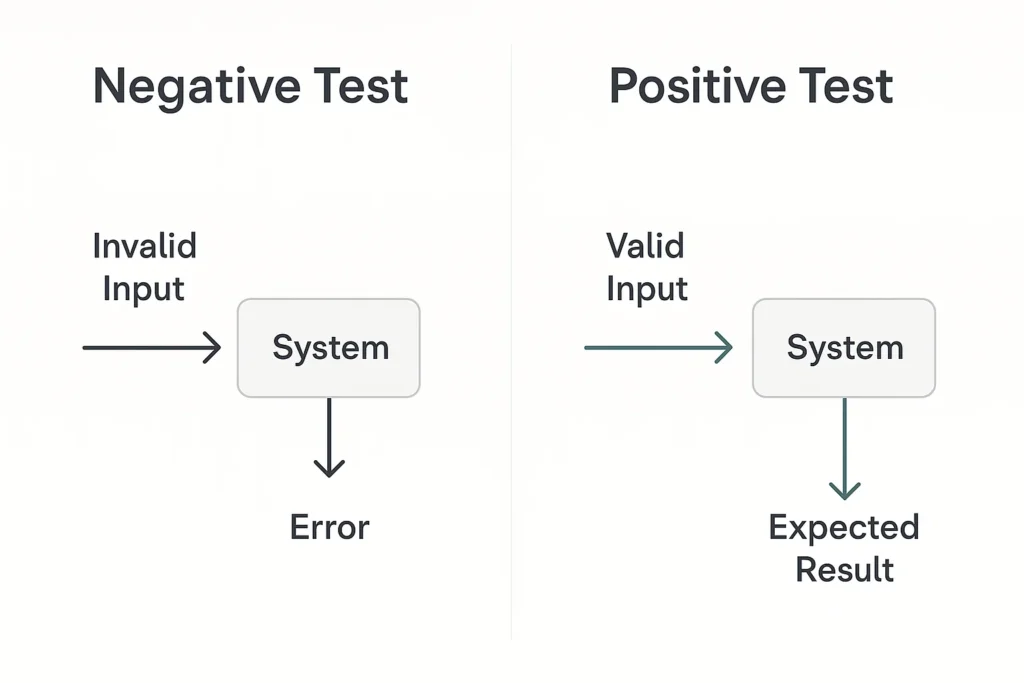
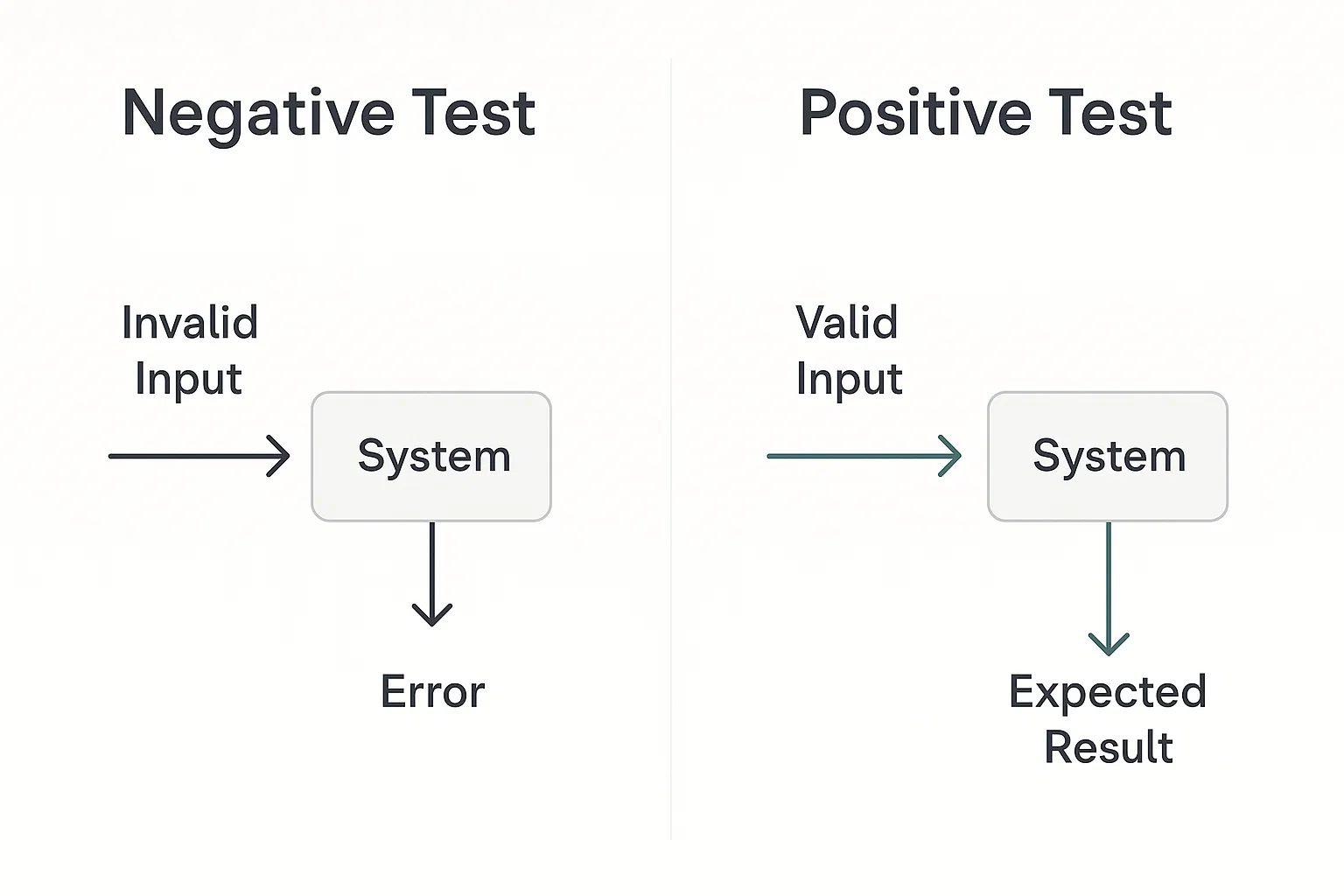
1. Negative vs. Positive Testing
Positive testing often called the “happy path” confirms that software behaves as intended when users supply valid input. If an email form accepts a properly formatted address and responds with a confirmation message, the positive test passes.
Negative testing, conversely, verifies that the same feature fails safely when confronted with invalid, unexpected, or malicious input. A robust application should display a friendly validation message when the email field receives john@@example..com, not a stack trace or, worse, a database error.
| S. No | Aspect | Positive Testing (Happy Path) | Negative Testing (Unhappy Path) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Goal | Confirm expected behaviour with valid input | Prove graceful failure under invalid, unexpected, or malicious input |
| 2 | Typical Data | Correct formats & ranges | Nulls, overflows, wrong types, special characters |
| 3 | Outcome | Works as designed | Proper error handling, no data leakage, solid security |
Transitioning from concept to reality, remember that robust software must be ready for both journeys.
2. Why Negative Scenarios Matter
First, broader coverage means code paths optimistic testers skip get tested. Second, early detection of critical errors slashes the cost of fixing them. Third and perhaps most crucial deliberate misuse targets authentication, authorisation, and data‑validation layers, closing doors that attackers love to pry open.
Business‑Level Impact
Consequently, these engineering wins cascade into tangible business outcomes:
- Fewer Production Incidents – Support tickets drop and SLAs improve.
- Lower Security Exposure – External pen‑test findings shrink, easing sales to regulated industries.
- Faster Compliance Audits – PCI‑DSS, HIPAA, GDPR auditors see documented due diligence.
- Accelerated Sales Cycles – Prospects gain confidence that the product will not break in production.
A customer‑satisfaction survey across 23 enterprise clients revealed that releases fortified with negative tests experienced a 38 % drop in post‑go‑live P1 defects and a 22 % reduction in external security findings. Clearly, negative testing is not a luxury it is insurance.

Prefer tailored advice? Book a free Sample QA audit with our senior architects and discover quick‑win improvements specific to your stack.
3. Key Techniques for Designing Negative Tests
Transitioning from benefits to execution, let’s explore five proven techniques that reliably expose hidden defects.
3.1 Exploratory Testing
Structured, time‑boxed exploration uncovers failure points before any automation exists. Begin with personas, say, an impatient user on a slow 3G network then probe edge cases and record anomalies.
3.2 Fuzz Testing
Fuzzing bombards an input field or API endpoint with random data to expose crashes. For instance, the small Python script below loops through thousands of printable ASCII payloads and confirms a predictable 400 Bad Request response.
import random, string, requests
payload = ''.join(random.choices(string.printable, k=1024))
resp = requests.post("https://api.example.com/v1/login", json={"password": payload})
assert resp.status_code == 400
3.3 Boundary‑Value & Equivalence Partitioning
Instead of testing every possible value, probe the edges -1, 0, and maximum + 1 where logic errors hide. Group inputs into valid and invalid classes so a handful of values covers thousands.
3.4 Session & Timeout Manipulation
Simulate expired JWTs, invalid CSRF tokens, and interrupted connections. By replaying stale tokens, you uncover weaknesses in state handling.
3.5 Database Integrity Checks
Attempt invalid inserts, orphan deletes, and concurrent updates to ensure the database enforces integrity even when the application layer misbehaves.
Tip: For every critical user story, draft at least one negative scenario during backlog grooming. Consequently, coverage rises without last‑minute scramble.
4. Best Practices for Planning and Execution
Next, let’s connect technique to process. Successful negative‑testing initiatives share five traits:
- Shift Left – Draft negative scenarios while writing acceptance criteria.
- Prioritise by Risk – Focus on payments, auth flows, and PII first.
- Align with Developers – Share the negative‑test catalogue so devs build defences early.
- Automate Smartly – Script repeatable scenarios; leave ad‑hoc probes manual.
- Document Thoroughly – Record inputs, expected vs. actual, environment, and ticket IDs.
Following this blueprint, one SaaS client integrated a 120‑case negative suite into GitHub Actions. As a direct result, the median lead time for change dropped from nine to six days because critical bugs now surface pre‑merge.
5. Sample Negative Test Edge Cases
Even a small set of well‑chosen edge‑case scenarios can reveal an outsized share of latent bugs and security flaws. Start with the following list, adapt the data to your own domain, and automate any case that would repay a second run.
- Blank mandatory fields: Submit all required inputs empty and verify the server rejects the request with a useful validation message.
- Extreme length strings: Paste 10,000‑character Unicode text (including emojis) into fields limited to 255 characters.
- Malformed email addresses: Try john@@example..com, john@example , and an address with leading/trailing spaces.
- Numeric overflows: Feed -1, 0, and max + 1 into fields whose valid range is 1‑99.
- SQL injection probes: Use a classic payload like‘ OR 1=1 — in text boxes and REST parameters.
- Duplicate submission: Double‑click the “Pay Now” button and ensure the backend prevents double‑charge.
- Network interruption midway: Disable connectivity after request dispatch; the UI should surface a timeout, not spin forever.
- Expired or forged JWT token: Replay a token issued yesterday or mutate one character and expect 401 Unauthorized.
- Stale CSRF token: Submit a form with an old token and confirm rejection.
- Concurrent modification: Update the same record from two browser sessions and look for deadlocks or stale‑state errors.
- File upload abuse: Upload a .exe or a 50 MB image where only small JPEGs are allowed.
- Locale chaos: Switch the browser locale to RTL languages or a non‑Gregorian calendar and validate date parsing.
Pro Tip: Drop each of these cases into your test‑management tool as a template set, then tag them to user stories that match the context.
Related Blogs
6. Common Pitfalls and How to Dodge Them
Transitioning to lessons learned, newbie teams often over‑correct or under‑invest.
| S. No | Pitfall | Why It Hurts | Rapid Remedy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Testing every imaginable invalid input | Suite bloat slows CI | Use equivalence classes to cut redundancy |
| 2 | Relying solely on client‑side checks | Attackers bypass browsers | Duplicate validation in API & DB layers |
| 3 | Sparse defect documentation | Devs burn hours reproducing | Capture request, response, and environment |
| 4 | Neglecting periodic review | Stale tests miss new surfaces | Schedule quarterly audits |
By steering around these potholes, teams keep negative testing sustainable.
7. From Theory to Practice: A Concise Checklist
Although every project differs, the following loop keeps quality high while keeping effort manageable.
Plan → Automate → Integrate → Document → Review
Highlights in bullet‑paragraph mix for quick scanning:
- Plan: Identify critical user stories and draft at least one negative path each.
- Automate: Convert repeatable scenarios into code using Playwright or RestAssured.
- Integrate: Hook scripts into CI so builds fail early on critical errors.
- Document: Capture inputs, environment, and ticket links for every failure.
- Review: Reassess quarterly as features and threat models evolve.
Conclusion
Negative testing is not an optional afterthought it is the guardrail that keeps modern applications from plunging into downtime, data loss, and reputational damage. By systematically applying the seven strategies outlined above shifting left, prioritising by risk, automating where it counts, and continuously revisiting edge cases you transform unpredictable user behaviour into a controlled, testable asset. The payoff is tangible: fewer escaped defects, a hardened security posture, and release cycles that inspire confidence rather than fear.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is negative testing in simple terms?
It is deliberately feeding software invalid input to prove it fails gracefully, not catastrophically.
-
When should I perform it?
Start with unit tests and continue through integration, system, and post‑release regression.
-
Which tools can automate Negative Scenarios?
Playwright, Selenium, RestAssured, OWASP ZAP, and fuzzing frameworks such as AFL.
-
How many negative tests are enough?
Prioritise high‑risk features first and grow coverage iteratively.
The post Negative Scenarios in Testing: Proven Ways to Bulletproof Your Software appeared first on Codoid.
Source: Read More