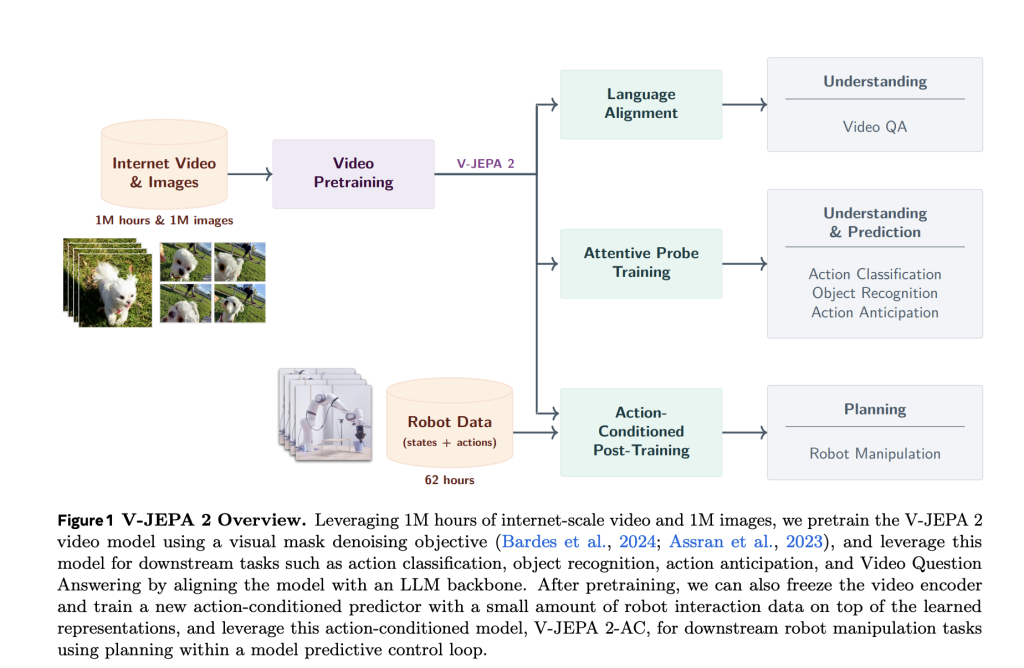
Meta AI has introduced V-JEPA 2, a scalable open-source world model designed to learn from video at internet scale and enable robust visual understanding, future state prediction, and zero-shot planning. Building upon the joint-embedding predictive architecture (JEPA), V-JEPA 2 demonstrates how self-supervised learning from passive internet video, combined with minimal robot interaction data, can yield a modular foundation for intelligent physical agents.

Scalable Self-Supervised Pretraining from 1M Hours of Video
V-JEPA 2 is pretrained on over 1 million hours of internet-scale video combined with 1 million images. Using a visual mask denoising objective, the model learns to reconstruct masked spatiotemporal patches in a latent representation space. This approach avoids the inefficiencies of pixel-level prediction by focusing on predictable scene dynamics while disregarding irrelevant noise.
To scale JEPA pretraining to this level, Meta researchers introduced four key techniques:
- Data scaling: Constructed a 22M-sample dataset (VideoMix22M) from public sources like SSv2, Kinetics, HowTo100M, YT-Temporal-1B, and ImageNet.
- Model scaling: Expanded the encoder capacity to over 1B parameters using ViT-g.
- Training schedule: Adopted a progressive resolution strategy and extended pretraining to 252K iterations.
- Spatial-temporal augmentation: Trained on progressively longer and higher-resolution clips, reaching 64 frames at 384×384 resolution.
These design choices led to an 88.2% average accuracy across six benchmark tasks—including SSv2, Diving-48, Jester, Kinetics, COIN, and ImageNet—surpassing previous baselines.
Understanding via Masked Representation Learning
V-JEPA 2 exhibits strong motion understanding capabilities. On the Something-Something v2 benchmark, it achieves 77.3% top-1 accuracy, outperforming models like InternVideo and VideoMAEv2. For appearance understanding, it remains competitive with state-of-the-art image-text pretraining models like DINOv2 and PEcoreG.
The encoder’s representations were evaluated using attentive probes, verifying that self-supervised learning alone can yield transferable and domain-agnostic visual features applicable across diverse classification tasks.
Temporal Reasoning via Video Question Answering
To assess temporal reasoning, the V-JEPA 2 encoder is aligned with a multimodal large language model and evaluated on multiple video question-answering tasks. Despite lacking language supervision during pretraining, the model achieves:
- 84.0% on PerceptionTest
- 76.9% on TempCompass
- 44.5% on MVP
- 36.7% on TemporalBench
- 40.3% on TOMATO
These results challenge the assumption that visual-language alignment requires co-training from the start, demonstrating that a pretrained video encoder can be aligned post hoc with strong generalization.
V-JEPA 2-AC: Learning Latent World Models for Robotic Planning
A key innovation in this release is V-JEPA 2-AC, an action-conditioned variant of the pretrained encoder. Fine-tuned using only 62 hours of unlabeled robot video from the Droid dataset, V-JEPA 2-AC learns to predict future video embeddings conditioned on robot actions and poses. The architecture is a 300M parameter transformer with block-causal attention, trained using a teacher-forcing and rollout objective.
This allows zero-shot planning through model-predictive control. The model infers action sequences by minimizing the distance between imagined future states and visual goals using the Cross-Entropy Method (CEM). It achieves high success in tasks such as reaching, grasping, and pick-and-place on unseen robot arms in different labs—without any reward supervision or additional data collection.

Benchmarks: Robust Performance and Planning Efficiency
Compared to baselines like Octo (behavior cloning) and Cosmos (latent diffusion world models), V-JEPA 2-AC:
- Executes plans in ~16 seconds per step (versus 4 minutes for Cosmos).
- Reaches a 100% success rate on reach tasks.
- Outperforms others in grasp and manipulation tasks across object types.

Notably, it operates using a monocular RGB camera without calibration or environment-specific fine-tuning, reinforcing the generalization capability of the learned world model.
Conclusion
Meta’s V-JEPA 2 represents a significant advancement in scalable self-supervised learning for physical intelligence. By decoupling observation learning from action conditioning and leveraging large-scale passive video, V-JEPA 2 demonstrates that general-purpose visual representations can be harnessed for both perception and control in the real world.
Check out the Paper, Models on Hugging Face and GitHub Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 99k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post Meta AI Releases V-JEPA 2: Open-Source Self-Supervised World Models for Understanding, Prediction, and Planning appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ