Language models have shown great capabilities across various tasks. However, complex reasoning remains challenging as it often requires additional computational resources and specialized techniques. This challenge has motivated the development of inference-time compute (ITC) scaling methods, which allocate additional computational resources to enhance model outputs during inference. The landscape of language model reasoning has evolved along two primary dimensions: approaches that boost reasoning capabilities during inference, and a new class of “reasoning models”. However, they introduce significant computational overhead, raising critical questions about efficiency and the optimal trade-off between computational resources and reasoning performance.
Inference-time scaling has emerged as a promising alternative to costly model pretraining. Inference-time architectures combining techniques such as generation ensembling, sampling, ranking, and fusion exceed individual model performance, as demonstrated by approaches like Mixture-of-Agents, LLM Blender, and orchestration frameworks like DSPy. Even techniques like chain-of-thought and branch-solve-merge enhance reasoning capabilities for single models. To reduce computational cost, methods like Confidence-Informed Self-Consistency (CISC) use confidence-weighted voting, cutting required samples significantly. Another technique, DivSampling, injects prompt perturbations to increase answer diversity, boosting performance across various tasks.
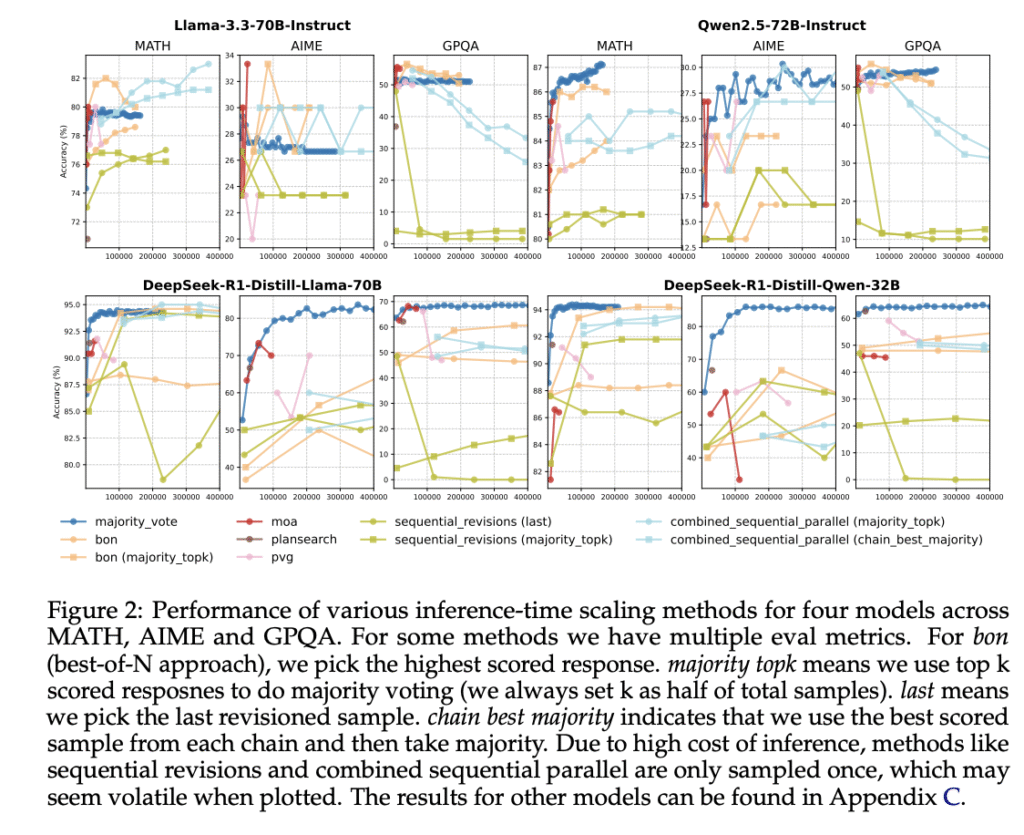
Researchers from Duke University, Together AI, the University of Chicago, and Stanford University have proposed a comprehensive analysis of inference-time scaling methods for both reasoning and non-reasoning models on challenging reasoning tasks. By constructing the Pareto frontier of quality and efficiency, the researchers discovered that non-reasoning models, even with extremely high inference budgets, still fall substantially behind reasoning models. For reasoning models, majority voting is a robust inference strategy, competitive with or outperforming other more complex ITC methods like best-of-N and sequential revisions. The researchers performed in-depth analyses of the association between key response features and response quality.
Researchers observed that R1-Distilled versions of Llama-3.3-70B significantly outperform their original Instruct counterparts. Despite using complex inference-time scaling methods, non-reasoning models fail to match the performance of purpose-built reasoning models. This empirical evidence suggests that for compute-optimal approaches, investing in training specialized reasoning models may provide substantially better long-term efficiency compared to repeated inference-time scaling of general models. Methods, including training-free, verifier-free inference-time scaling methods, offer minimal improvements for reasoning models. Almost all methods underperform majority voting for both DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32 B.
Non-reasoning models show the clear absence of correlation between response length and correctness across most tasks, with response length gaps being consistently low. The only exception is Llama-3.1-8 B-Instruct, which displays a non-negligible gap for the AIME task. In contrast, reasoning models demonstrate a clearer trend where shorter, more precise responses tend to be more accurate, providing evidence of an inverse relationship between response length and accuracy. This phenomenon reflects the complex reasoning mechanisms inherent in these models. Moreover, analysis of the MATH dataset, with its natural difficulty gradient, confirms that reasoning models tend to generate more accurate responses with shorter lengths for high-difficulty problems.
In conclusion, researchers thoroughly evaluate verifier-free inference-time scaling methods for LLMs, emphasizing their efficiency and effectiveness in reasoning tasks. Despite using advanced scaling techniques and significant computational resources, non-reasoning models consistently lag behind specialized reasoning models like R1-Distilled Models. For reasoning models, simpler strategies such as majority voting often surpass more intricate methods like best-of-N or sequential revisions in performance. Moreover, the correct responses are shorter and feature fewer linguistic markers, indicating these traits could serve as predictors of accuracy. Utilizing these response characteristics and linguistic marker features to enhance inference methods can be an intriguing future direction.
Check out the Paper. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Optimizing Reasoning Performance: A Comprehensive Analysis of Inference-Time Scaling Methods in Language Models appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop