Discovering faster algorithms for matrix multiplication remains a key pursuit in computer science and numerical linear algebra. Since the pioneering contributions of Strassen and Winograd in the late 1960s, which showed that general matrix products could be computed with fewer multiplications than previously believed, various strategies have emerged. These include gradient-based methods, heuristic techniques, group-theoretic frameworks, graph-based random walks, and deep reinforcement learning. However, significantly less focus has been placed on matrix products with inherent structure, such as when the second matrix is the transpose or identical to the first, or when matrices possess sparsity or symmetry. This oversight is notable, given that expressions like AA^T appear frequently in domains such as statistics, deep learning, and communications, representing critical constructs like Gram and covariance matrices. Moreover, XX^T is repetitive in large language model training algorithms like Muon and Shampoo.
Previous studies have explored structured matrix multiplication using various theoretical and machine learning-based methods. Representation theory and the Cohn–Umans framework have been employed to design efficient multiplication schemes for structured matrices. Reinforcement learning has also shown promise—models have learned to discover or rediscover known algorithms like Strassen’s. Recent work has focused on optimizing the computation of XX^T over finite fields and complex domains. Among these, the most efficient known method for real-valued XX^T is Strassen’s algorithm, who apply Strassen’s algorithm recursively on 2×2 block matrices, effectively translating the structured problem back into the domain of general matrix multiplication.
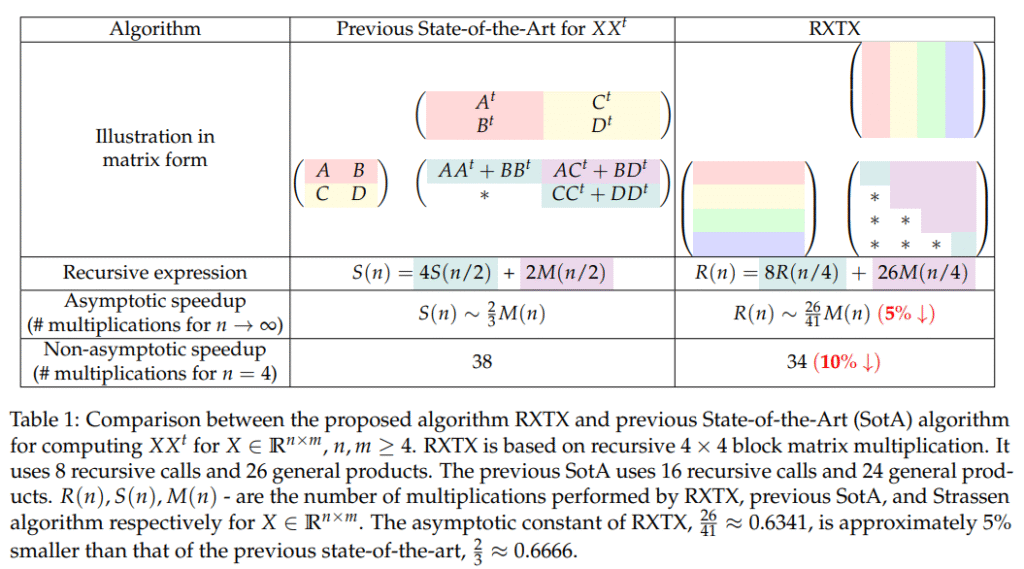
Researchers from the Chinese University and the Shenzhen Research Institute of Big Data have developed RXTX, an algorithm for efficiently computing XX^T where X belongs to R^n*m. RXTX reduces the number of required operations—multiplications and additions—by approximately 5% compared to the current leading methods. Unlike many algorithms that only show benefits for large matrices, RXTX delivers improvements even for small sizes (e.g., n = 4). The algorithm was discovered through machine learning-based search and combinatorial optimization, leveraging the specific structure of XX^T for constant-factor acceleration.
The RXTX algorithm improves matrix multiplication by reducing the number of operations compared to previous methods like recursive Strassen and Strassen-Winograd. It uses 26 general matrix multiplications and optimized addition schemes, resulting in fewer total operations. Theoretical analysis shows RXTX performs fewer multiplications and combined operations, especially for larger matrices. Practical tests on 6144 × 6144 matrices using a single-thread CPU show RXTX is about 9% faster than standard BLAS routines, with speedups observed in 99% of runs. These results highlight RXTX’s efficiency for large-scale symmetric matrix products and its advantage over traditional and state-of-the-art recursive algorithms.
The proposed methodology integrates RL with a two-tier Mixed Integer Linear Programming (MILP) pipeline to discover efficient matrix multiplication algorithms, particularly for computing XX^T. The RL-guided Large Neighborhood Search generates a large set of potential rank-1 bilinear products, which are candidate expressions. MILP-A explores all linear combinations of these products to express the target outputs, while MILP-B identifies the smallest subset that can represent all targets. This setup mirrors the AlphaTensor approach but simplifies it by reducing the action space significantly, focusing on lower-dimensional tensor products and leveraging MILP solvers like Gurobi for rapid computation.
For example, to compute XX^T for a 2×2 matrix X, the goal is to derive expressions like x_1^2 + x_2^2 or x_1x_3 + x_2x_4. The RL policy randoMLy samples thousands of bilinear products using coefficients from {−1, 0, +1}. MILP-A finds combinations of these products that match the desired expressions, and MILP-B selects the fewest needed to cover all targets. This framework enabled the discovery of RXTX, an algorithm that performs 5% fewer multiplications and overall operations than prior methods. RXTX is efficient for large and small matrices and demonstrates a successful fusion of ML-based search and combinatorial optimization.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 95k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post RXTX: A Machine Learning-Guided Algorithm for Efficient Structured Matrix Multiplication appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ