Limitations of Traditional Climate Modeling
Earth system models are essential tools for forecasting environmental changes and helping us prepare for the future. However, their high computational demands make it difficult to run them at resolutions fine enough for detailed, local predictions. Currently, most models are limited to a resolution around 100 kilometers—roughly the size of Hawai’i—making it hard to generate accurate projections for specific regions. Yet, city-scale forecasts at approximately 10 kilometers are vital for real-world applications, such as agriculture, water resource planning, and disaster preparedness. Improving the resolution of these models is key to better protecting communities and supporting more effective local decision-making.
Introducing Dynamical-Generative Downscaling with AI
Researchers at Google have introduced a method that combines traditional physics-based climate modeling with generative AI to assess regional environmental risks. Published in PNAS, their approach—called dynamical-generative downscaling—utilizes diffusion models, a type of AI that learns complex patterns, to convert broad global climate projections into detailed, local predictions at a resolution of approximately 10 km. This method not only bridges the gap between large-scale models and real-world decision-making needs but also does so far more efficiently and affordably than current high-resolution techniques, making it feasible to apply across the growing volume of climate data now available.
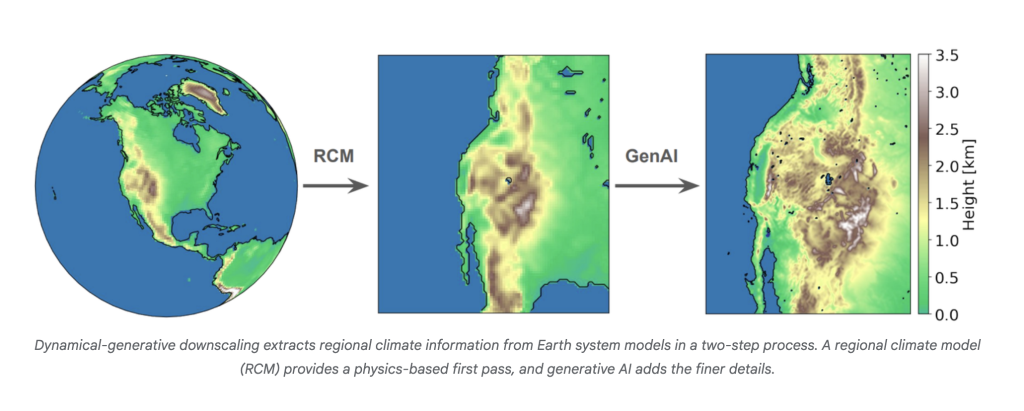
To better understand local environmental changes at fine resolutions (around 10 km), scientists typically use a method called dynamical downscaling. This process takes broad data from global climate models and refines it using regional climate models, like zooming in on a worldwide map to see more detail. While this technique provides highly accurate local forecasts by factoring in terrain and regional weather patterns, it comes at a steep computational cost, making it too slow and expensive to apply broadly across many climate scenarios. Simpler statistical methods are faster but often fail to model extreme events or reliably adapt to new future conditions.
Improving Accuracy and Efficiency with R2D2
To overcome these challenges, researchers have introduced a more efficient method that merges the strengths of physics-based models with generative AI. This two-step process begins with a physics-based simulation that downscales global data to a mid-level resolution, ensuring consistency across different global models. Then, a generative AI model called R2D2 fills in the finer details—like small-scale weather features shaped by terrain—by learning from high-resolution examples. By focusing on the differences between medium and high resolutions, R2D2 improves accuracy and generalizes well to unseen scenarios. This combined approach enables faster, cost-effective, and realistic local climate projections across a wide range of future scenarios.
To test the new approach, researchers trained the model using one high-resolution climate projection from the Western U.S. and then evaluated it on seven others. Compared to traditional statistical methods, their AI-powered downscaling model significantly reduced errors by over 40% in predicting variables like temperature, humidity, and wind. It also more accurately captured complex weather patterns, like heatwaves combined with droughts or wildfire risks from strong winds. This method enhances both accuracy and efficiency, providing more accurate estimates of extreme weather and uncertainty while utilizing only a fraction of the computing power required by traditional high-resolution simulations.

In conclusion, the new AI-powered downscaling approach is a major leap forward in making detailed, regional climate forecasts more accessible and affordable. By combining traditional physics-based modeling with generative AI, the method delivers accurate, city-scale (~10 km) climate risk assessments while cutting computing costs by up to 85%. Unlike older methods, which are limited by scale and expense, this technique can efficiently handle large ensembles of climate projections. It captures uncertainties more comprehensively and supports smarter planning in agriculture, disaster preparedness, water management, and infrastructure. In short, it turns complex global data into actionable local insights—faster, cheaper, and more accurately than ever before.
Check out the Paper and Technical details. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 99k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post Google AI Unveils a Hybrid AI-Physics Model for Accurate Regional Climate Risk Forecasts with Better Uncertainty Assessment appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ